MICROELECTRONICS and NANOTECHNOLOGY (MN)
Question 3: Field Effect Devices
August 2012
Questions
All questions are in this link
Solutions of all questions
a)$ \begin{align*} C_1&=C_{ox}=\frac{\epsilon_0\epsilon_{ox}}{t_{ox}}\\ \therefore t_{ox}&=\frac{20\epsilon_0}{C_1} \end{align*} $
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
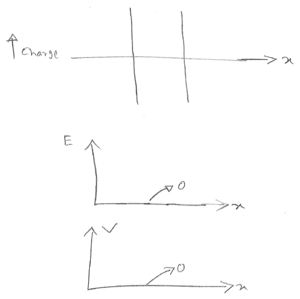
b)i) $ V_{GS} =0 $
ii) $ V_{GS} = 0.5V; $ dep/inv transition (from C-V curve)
iii) $ V_{GS} = 1V; $ inversion
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
c)$ V_{th} = 0.5V $. Lowest value of C.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
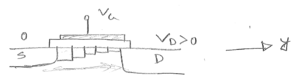
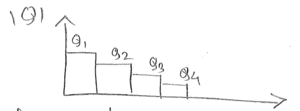
Drift current;
$ \begin{align*} J_1&=Q_1\mu\epsilon_1=Q_1\mu\frac{dV}{dy}\vert_1\\ J_2&=Q-2\mu\frac{dV}{dy}\vert_2\\ J_3&=Q_3\mu\frac{dV}{dy}\vert_3 \end{align*} $
$ \sum_{i=1}^N\frac{J_idy}{\mu} = \sum_{i=1}^NQ_idV $
$ \begin{align*} &\implies \frac{J_D}{\mu}\sum_{i=1}^Ndy = \int_0^{V_d}C_{ox}(V_G-V_{th}-mV)dV\\ &\implies \frac{J_D}{\mu}L=C_{ox}(V_G-V_{th})V_d-m\frac{V_d^2}{2}\\ &\therefore J_D=\frac{\mu C_{ox}}{L}\bigg[(V_G-V_{th})V_d-m\frac{V_d^2}{2}\bigg] \end{align*} $
$ \begin{align*} \therefore I_D&=W\cdot J_D\\ &=\mu C_{ox}\frac{W}{L}\bigg[(V_G-V_{th})V_d-m\frac{V_d^2}{2}\bigg] \end{align*} $
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
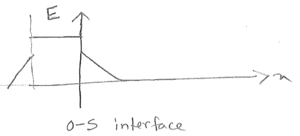
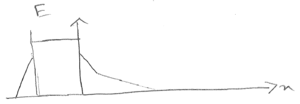
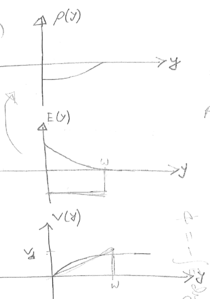
f) $ \begin{align*} L_{min}&=\frac{V_d}{E_{crit}} = \frac{3V}{10^4 V/cm \text{ from curve}}\\ &=3\times10^{-4}cm \end{align*} $
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
g) $ V_T \downarrow $ for short channel
$ I_{DSTAT}\uparrow $ as $ \sim(V_{GS}-V_{th}) $
$ V_{DSTAT}\uparrow $ as $ \sim(V_{GS}-V_{th}) $
(* quantitative how??)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------