Contents
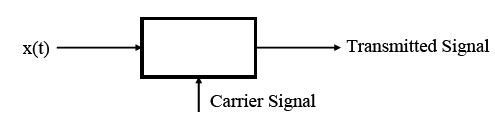
the concept of modulation
•More efficient to transmit E&M signals at higher frequencies
•Transmitting multiple signals through the same medium using different carriers
•Transmitting through “channels” with limited passbands
•Others...
How?
•Manymethods
•Focus here for the most part on Amplitude Modulation (AM)
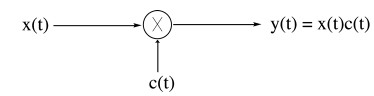
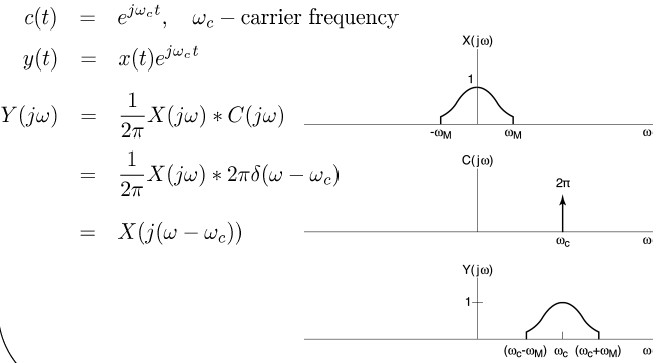
Amplitude Modulatioin of a Complex Exponential Carrier
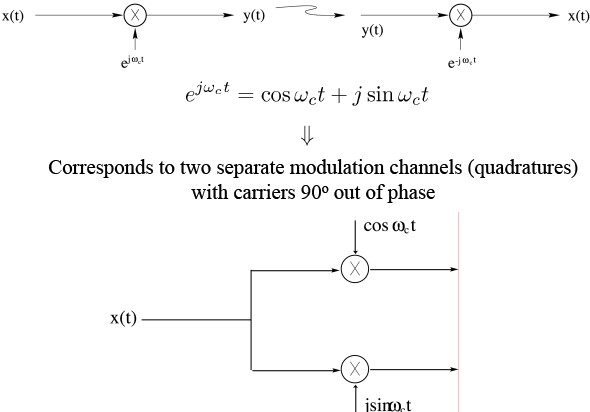
Demodulation of Complex Exponential AM
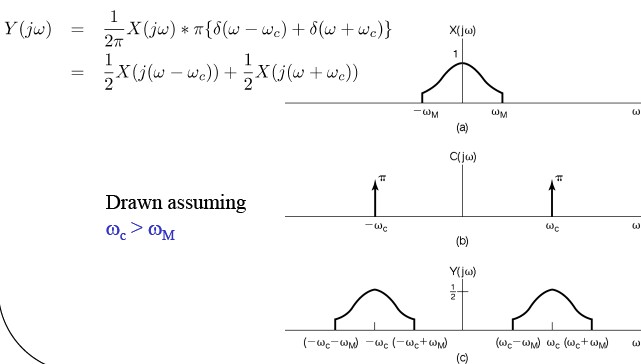
Sinusoidal AM
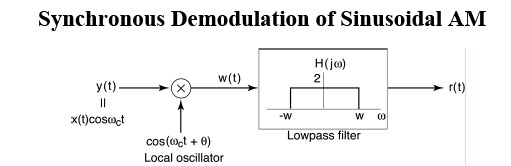
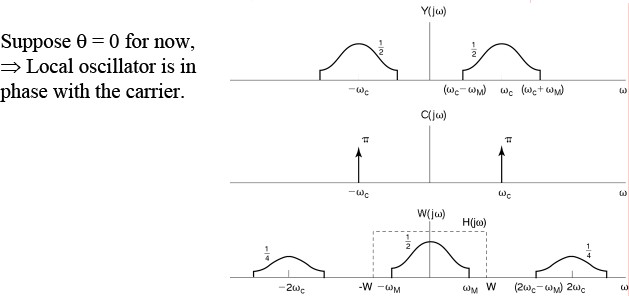
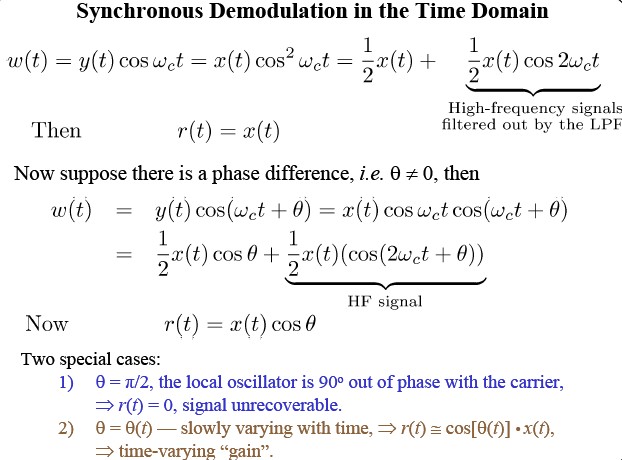
Synchronous Demodulation (with phase error) in the Frequency DomainAgain
Demodulating signal has phase difference θw.r.t.the modulating signal
$ cos(\omega_{C}t+\theta)= \frac{1}{2}e^{j\theta}e^{j\omega_{c}t}+\frac{1}{2}e^{-j\theta}e^{-j\omega_{c}t} $
fourier ====> $ \pie^{j/theta}/delta(/omega-/omega_{c})+/pie^{-j/theta}/delta(/omerga-/omerga_{c}) $