Contents
Similarity analysis of images
Look at the Mona Lisa(s) above. They are very similar, aren't they? It's obvious, and you can say that they have high similarity. But given the pictures below, how to determine the similarity? Let's see!
Introduction & Background
Generally, there are two criteria to determine image similarity, the coefficient of determination (R2) and the mean absolute error (MAE). Here in this project, I use the coefficient of determination for similarity analysis.
The computation of R2 is:
$ R2 = 1 - {\sum_{i=1}^N (y_i - y_{pre})^2 / \sum_{i=1}^N (y_i - y_{avg})^2 } $ ( 1 )
or $ R2 = \frac{SS_{xy}^2}{SS_{xx} SS_{yy} } $ ( 2 )
where $ SS_{xy} = \sum_{i=1}^N (y_i - y_{avg})(x_i - x_{avg}) $ ( 3 )
$ SS_{yy} = \sum_{i=1}^N (y_i - y_{avg})^2 $ ( 4 )
$ SS_{xx} = \sum_{i=1}^N (x_i - x_{avg})^2 $ ( 5 )
Where N is the total number of the components. x is the value of reference image, y is the value of the other image. xavg is the mean of the x values and yavg is the mean of the y values.
The meaning of R2: R2 value varies from 0 to 1. 1 means perfect fit between models, 0 means very poor fit; a good fit if R2 >0.8, and poor fit if R2<0.3.
I think to compute the similarity between models, two components should be considered : the vein and luminance. I use the color histogram to determine the similarity of luminance and slope to determine the similarity of vein.
The slope magnitude within a 3 x 3 mask is defined as follows:
$ S_k(i, j) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll}|P(i, j) - P(ii, jj)| & \text{ if } (i = ii \text{ and } \ j \neq jj \ )\text{ or }(j = jj \text{ and } \ i \neq ii \ ) \\ |P(i, j) - P(ii, jj)|/\sqrt2 & \text{ if } (\ i \neq ii \ \text{ and } \ j \neq jj \ )\end{array}\right. $ ( 6 )
S(i, j) = Max[Sk(i, j)] k = 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 ( 7 )
where S(i, j) is the value of the slope magnitude at location (i, j), P(i, j) is the pixel intensity value at location (i, j)
Here's the fun part! Lol
(a) 


(b) 

(c) 

(d) 

Look at set (a). chair1.jpg looks 'darker' than chair2.jpg and chair3.jpg. But chair1, chair2 and chair3 have very similar structure.
For set (b), they look almost the same expect that computer2.jpg is brighter.
Set (c) is interesting, from student1.jpg to student2.jpg, the images has been shifted; but the luminance look similar.
Set (d) is special. First, Yimin is quite large in the picture (1/3 of the image). Second, the picture is kind blurred (I took the picture using my phone).
Let's see the similarity between those images!
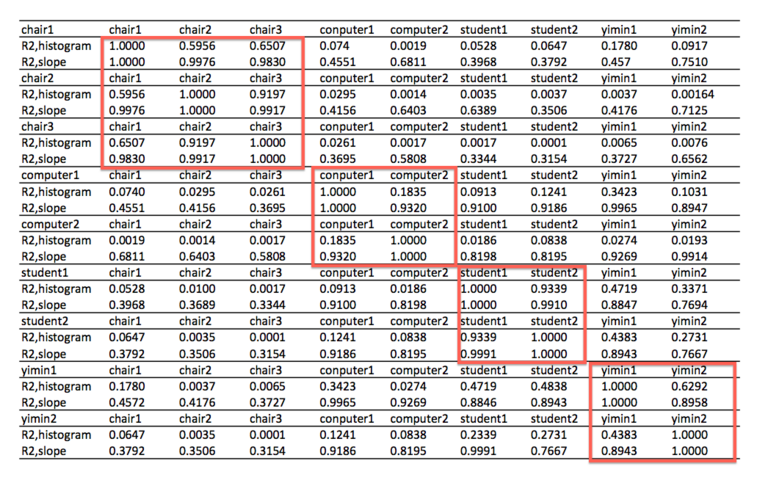
Table 1: Similarity analysis results using the coefficient of determination
Results analysis
For set(a), chair1 is not similar with chair2 or chair3 in
...to be continued