Contents
ECE 438
Q: What is ECE 438 about?
A: Digital signals and systems.
Q: What is a digital signal?
A: A signal that can be represented by a sequence of 0's and 1's.
- The signal must be discrete time (D.T.):
- x[n], n e Z
- The signal values must come from a discrete and finite signal.
- e.g. x[n] e {0,1}
- e.g. x[n] e {0,1,2,3,...,255} (grayscale values)
The Digital System
Three main types:
- Software (MATLAB, C program)
- Firmware
- Hardware
Advantages of Digital Signals & Systems
Digital Systems are:
- Precise
- Reproducible
- Easy to build
- Adaptable
- Easy to upgrade/fix
- Can be saved on a bistable storage device
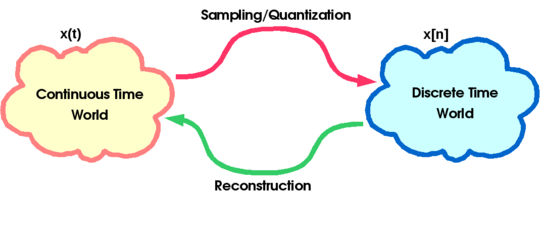
The Continuous Time World and The Discrete Time World
The Continuous Time (C.T.) World
- Most natural signals live here
- Things are intuitive
- Easy math
The Discrete Time (D.T.) World
- Digital media lives here, along with computers, MATLAB, and digital circuits.