(Created page with "'''1. (15% of Total)''' This question is a set of short-answer questions (no proofs): '''(a) (5%)''' State the definition of a Probability Space. '''Answer''' You can see...") |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 23:52, 9 March 2015
1. (15% of Total)
This question is a set of short-answer questions (no proofs):
(a) (5%)
State the definition of a Probability Space.
Answer
You can see the definition of a Probability Space.
(b) (5%)
State the definition of a random variable; use notation from your answer in part (a).
Communication, Networking, Signal and Image Processing (CS)
Question 1: Probability and Random Processes
August 2003
Answer (74p on Papoulis)
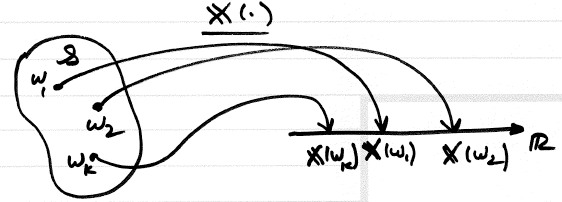
A random variable $ \mathbf{X} $ is a process of assigning a number $ \mathbf{X}\left(\xi\right) $ to every outcome $ \xi $ . The result function must satisfy the following two conditions but is otherwise arbitrary:
1. The set $ \left\{ \mathbf{X}\leq x\right\} $ is an event for every $ x $ .
2. The probabilities of the events $ \left\{ \mathbf{X}=\infty\right\} $ and $ \left\{ \mathbf{X}=-\infty\right\} $ equal 0.
Answer (Intuitive definition)
Given $ \left(\mathcal{S},\mathcal{F},\mathcal{P}\right) $ , a random variable $ \mathbf{X} $ is a mapping from $ \mathcal{S} $ to the real line. $ \mathbf{X}:\mathcal{S}\rightarrow\mathbb{R} $ .
(c) (5%)
State the Strong Law of Large Numbers.
Answer
You can see the definition of the Strong Law of Large Numbers.