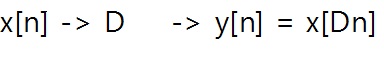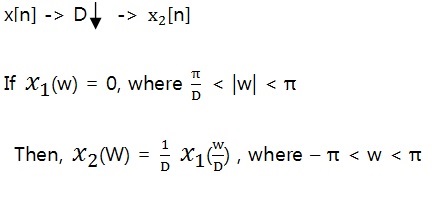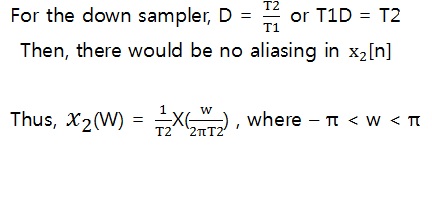| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
===== <br> Downsampling reduces the magnitude by a factor of D, and increases the width of signals by D in the frequency domain. Moreover, it repeats it's signals every 2π and to prevent aliasing, decimator needs a lowpass filter before the downsampling. ===== | ===== <br> Downsampling reduces the magnitude by a factor of D, and increases the width of signals by D in the frequency domain. Moreover, it repeats it's signals every 2π and to prevent aliasing, decimator needs a lowpass filter before the downsampling. ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Downsampling_Soonho_Kwon_slecture_review|Questions and comments]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them on [[Downsampling_Soonho_Kwon_slecture_review|this page]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 05:07, 13 October 2014
Contents
- 1 1. Introduction
- 1.1 Sampling is essential to convert analog signal to digital signal. In this page, I would specificallyexplain about downsampling. In digital signal processing, the decimator performs decimation, which isdownsampling a signal. In other words, when a digital signal is downsampled, the signal's samplingrate would be reduced.
- 1.2
- 2
- 3 2. Derivation
- 4
- 5 3. Example
- 6 If) D = 2
- 7
- 8
- 9 4. Conclusion
1. Introduction
Sampling is essential to convert analog signal to digital signal. In this page, I would specifically
explain about downsampling. In digital signal processing, the decimator performs decimation, which is
downsampling a signal. In other words, when a digital signal is downsampled, the signal's sampling
rate would be reduced.
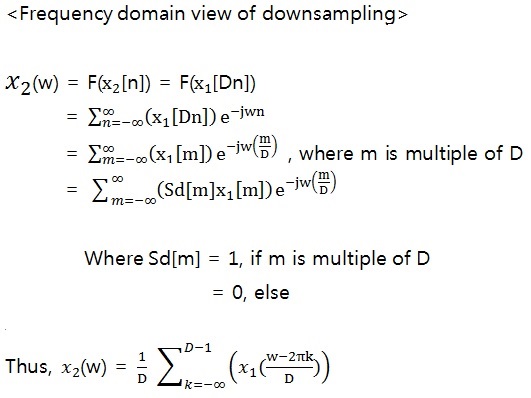
2. Derivation
3. Example
If) D = 2
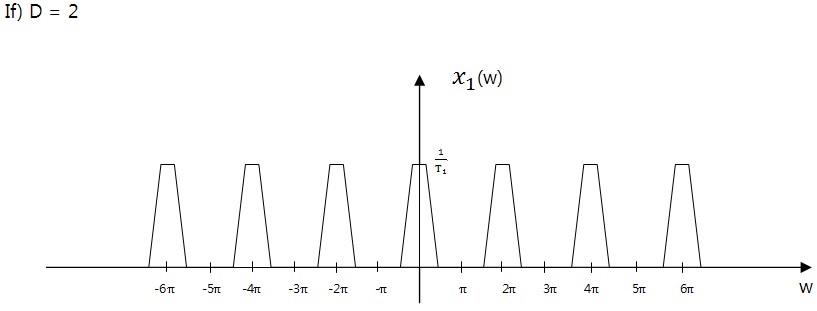
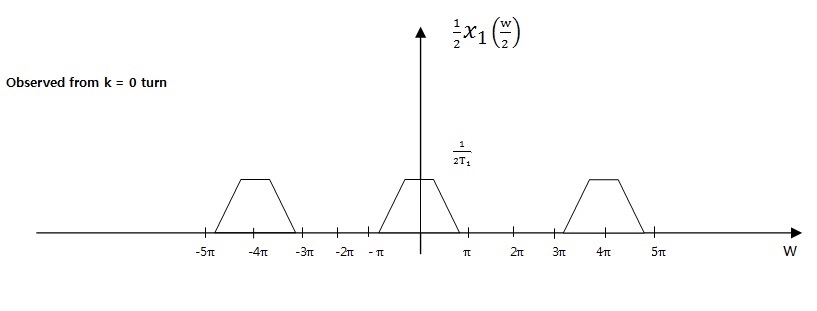
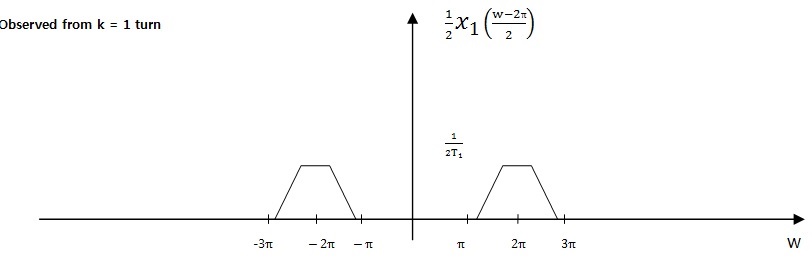
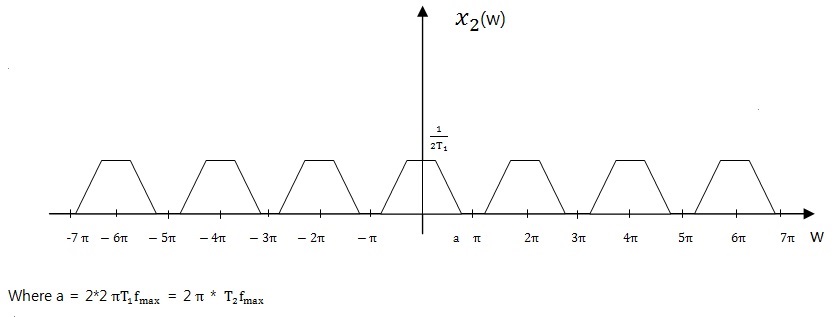
4. Conclusion
Downsampling reduces the magnitude by a factor of D, and increases the width of signals by D in the frequency domain. Moreover, it repeats it's signals every 2π and to prevent aliasing, decimator needs a lowpass filter before the downsampling.
Questions and comments
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them on this page.