| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | '''Theory'''<br> | + | '''Theory'''<br> Upsampling in the frequency domain<br> <br> [[Image:Theroy.jpg]] '''or ''' [[Image:CodeCogsEqn.jpg]] |
| − | Upsampling in the frequency domain<br> | + | |
| − | <br> [[Image:Theroy.jpg]] '''or ''' [[Image:CodeCogsEqn.jpg]] | + | |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 39: | ||
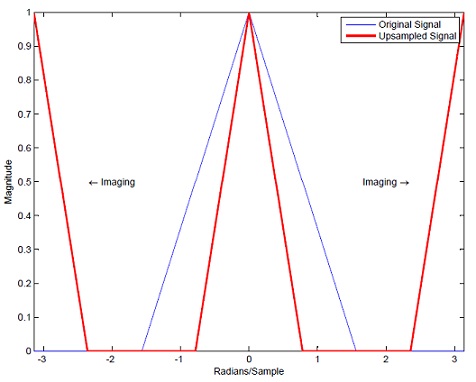
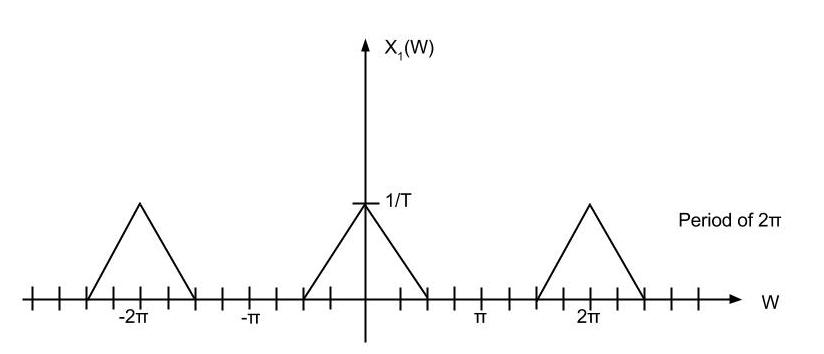
Upsampling rate D = 2 | Upsampling rate D = 2 | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> |
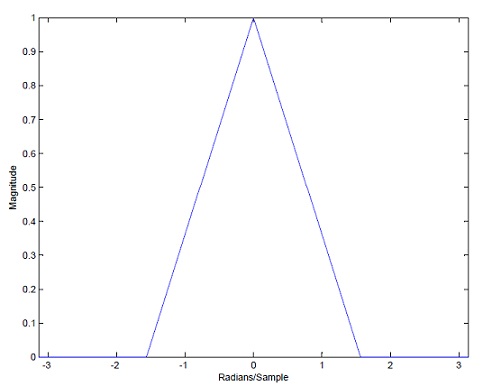
| − | Here is the sampled signal.<br> | + | Here is the sampled signal.<br> |
[[Image:Graphex.jpg]] | [[Image:Graphex.jpg]] | ||
| Line 57: | Line 55: | ||
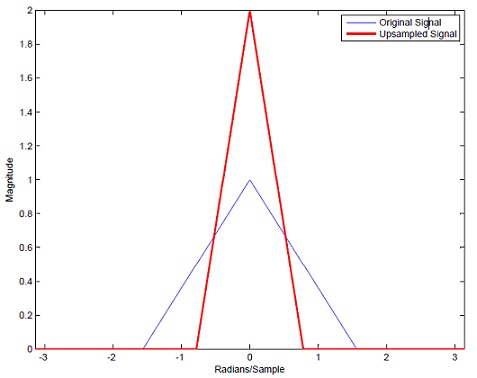
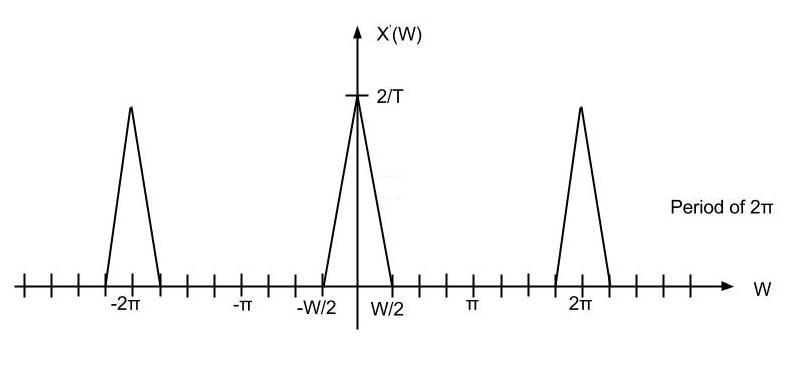
Final upsampled signal<br> | Final upsampled signal<br> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Graphex5.jpg]] |
'''Conclusion''' | '''Conclusion''' | ||
Revision as of 07:07, 10 October 2014
OUTLINE
1. Introduction
2. Theory
3. Example
4. Conclusion
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Introduction
Upsampling is the process of increasing sampling rate.
Theory
Upsampling in the frequency domain
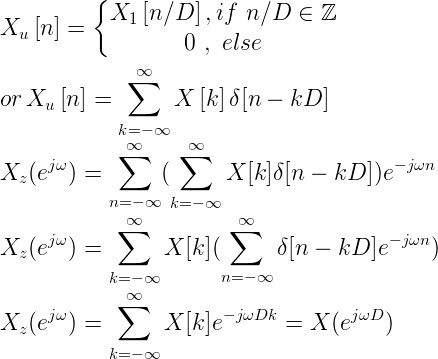 or
or 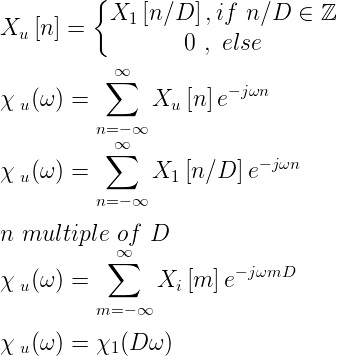
Example
Upsampling rate D = 2
Here is the sampled signal.
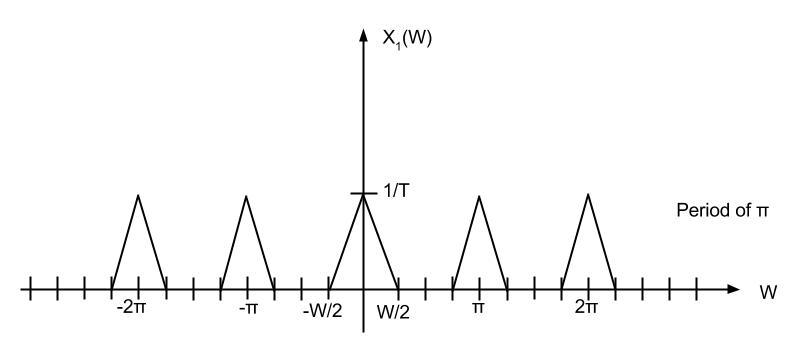
Upsampling rate D = 2 is applied.
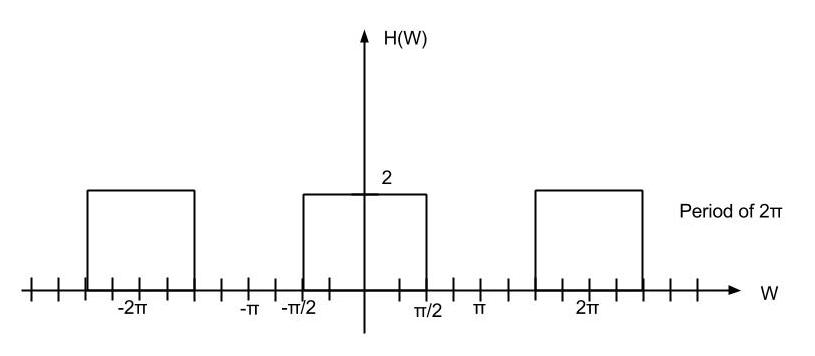
Low-Pass filter of cutoff π/2, gain 2 is applied.
Final upsampled signal
Conclusion