| Line 206: | Line 206: | ||
National popular voting plan (NPV) is started in purposing of making every vote same. It’s based on two state powers established in U.S. Constitution: states have plenary power to decide how to apportion their electoral votes and the states have the power to enter into binding interstate compacts. It has been introduced by state legislators in all 50 states and District of Columbia in December 2010. To join this plan, the legislators have to pass National Popular Vote Bill and signed it into law. | National popular voting plan (NPV) is started in purposing of making every vote same. It’s based on two state powers established in U.S. Constitution: states have plenary power to decide how to apportion their electoral votes and the states have the power to enter into binding interstate compacts. It has been introduced by state legislators in all 50 states and District of Columbia in December 2010. To join this plan, the legislators have to pass National Popular Vote Bill and signed it into law. | ||
| − | Currently, NPV is the most popular voting method candidate with the most supports to replace electoral votes. It is now proposed and waiting for votes. To make this proposal into effect, it needs 270 or more electoral votes to agree this system. As the latest news, Rhode Island Governor Lincoln Chafee signs National Popular Vote bill in July 2013. And after that, there are 10 jurisdictions possessing 136 electoral votes (50.4% of the 270 electoral votes) in total joining this plan. Besides, at least one legislative chamber in 21 states (including AR, CO, CT, DE, ME, MI, NV, NM, NY, NC, and OR) have passed this bill. There are 2124 state legislators have endorsed the bill. | + | Currently, NPV is the most popular voting method candidate with the most supports to replace electoral votes. It is now proposed and waiting for votes. To make this proposal into effect, it needs 270 or more electoral votes to agree this system. As the latest news, Rhode Island Governor Lincoln Chafee signs National Popular Vote bill in July 2013. And after that, there are 10 jurisdictions possessing 136 electoral votes (50.4% of the 270 electoral votes) in total joining this plan. Besides, at least one legislative chamber in 21 states (including AR, CO, CT, DE, ME, MI, NV, NM, NY, NC, and OR) have passed this bill. There are 2124 state legislators have endorsed the bill.<br> |
| − | + | ||
| − | <br> | + | |
*10 jurisdictions signed the National popular Vote bill into law<br> | *10 jurisdictions signed the National popular Vote bill into law<br> | ||
| Line 261: | Line 259: | ||
[[Image:Ma279 vote.png|650x75px]]<br> | [[Image:Ma279 vote.png|650x75px]]<br> | ||
| − | <u></u><br> | + | <u></u><br> |
| − | <u>Pros and Cons</u> | + | <u>Pros and Cons</u> |
The pros and cons of NPV are still under discussion. Same as its current support rate, not all people think this is better than current voting system -- electoral votes, though it may caused the “unwilling” candidate becomes the president. | The pros and cons of NPV are still under discussion. Same as its current support rate, not all people think this is better than current voting system -- electoral votes, though it may caused the “unwilling” candidate becomes the president. | ||
| Line 269: | Line 267: | ||
Supporters of NPV claim that this voting system will, obviously, give a fairer result. This can intuitively present the supporting rate of all candidates, and never let a candidate who lost the popular vote win as it original purpose. Meanwhile, they argued that the candidates put too much emphasis on large swing states and therefore negating smaller states under electoral votes system. <br>However, critics give different comments. They believe that NPV will discourage candidates from campaigning and paying attention to sparsely populated regions of the country. This will lead the problem that the rural America is neglected and densely populated cities, for example, are focused too intently. <br> | Supporters of NPV claim that this voting system will, obviously, give a fairer result. This can intuitively present the supporting rate of all candidates, and never let a candidate who lost the popular vote win as it original purpose. Meanwhile, they argued that the candidates put too much emphasis on large swing states and therefore negating smaller states under electoral votes system. <br>However, critics give different comments. They believe that NPV will discourage candidates from campaigning and paying attention to sparsely populated regions of the country. This will lead the problem that the rural America is neglected and densely populated cities, for example, are focused too intently. <br> | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> |
== Conclusion<br> == | == Conclusion<br> == | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 25 November 2013
Contents
Presidents and others that have been elected against majority
By Antong Li, Mengyao Wang, Chenlin Zhou, and Yi Hu.
Introduction
.....
Direct election
Direct election means voters choose the officeholders directly. The most commonly used systems are plurality system and two round system. Examples of direction election are the European Parliament and the United States Senate.
Indirect election
By contrast, in an indirect election, rather than voting for officeholders directly, they vote for electors, and the officeholders were finally decided by the electors voted by the voters. It is widely used in many union elections Because voters don’t vote for the the candidates directly, there will be occasions that candidates are elected without popularity, or the majority.
The United States president election is a typical indirect election system. Throughout the history of United States, four presidents were elected without winning popular votes.
Presidents election in United States
Election process
According to Article II of the United States Constitution,
“Article II
Section 1. The executive power shall be vested in a President of the United States of America. He shall hold his office during the term of four years, and, together with the Vice President, chosen for the same term, be elected, as follows:
...No person except a natural born citizen, or a citizen of the United States at the time of the adoption of this Constitution, shall be eligible to the office of President neither shall any person be eligible to that office who shall not have attained to the age of thirty five years, and been fourteen Years a resident within the United States.”,
a person has to meet the following requirements to be a candidate for the presidency:
- At least 35 years old
- A natural born citizen
- A resident of the United States for 14 years
There will be many candidates for the presidency every year, and everyone has their own political views and preferable parties. Some of them will have similar ideas, so usually there are more than one candidate in the same political party. However, each party should only has one candidate to run for President. Therefore, a nominating process is needed for every parties. A series of the presidential primary elections and caucuses held in each state and territory in U.S, and presidential nominating conventions held in each political party are two main ideas to select one final nominee. (There are some people decide to run for the President without being a part of any political party, but such independent candidates need other requirement to stay on the campaign)
After the above selections, there should be only one Presidential nominee in each party. In the same time, this candidate need to choose a Vice-Presidential candidate to run the election together. Voters should consider them as a whole team, so they cannot choose a Presidential candidate from one party and a Vice-Presidential candidate from another party.
Now, it is time for general election and electoral college election. Nevertheless, by very rare chance, if no presidential candidate receives more than half of the electoral votes, then the House of Representatives will choose the President among the top three presidential candidates and the Senate will choose the Vice-President among the top two candidates. (This happens in 1824 for President John Quincy Adams)
the Popular Election
In the popular election, every citizen who is at legal age can vote. As a direct vote described in the beginning of this article, popular election is not how the United States President is chosen. The Founding Fathers of the United States of America thoughts direct vote was too chaotic and easy to make mistake. Instead, they designed a new electoral college system.
the Electoral college
The United States electoral college is the institution which elected president and vice president every four years. According to article II of the United States Constitution,
Electors are appointed to each states and the district of columbia. There are 538 electors in total, 435 of which are representatives, 100 senators, and 3 electors from District of Columbia. The number of electors in each State is the same as the number of members in Congress.
Electors are pledged to particular presidential and vice presidential candidates, though unpledged electors are possible. In most of the states, electors are elected on a ‘winner-take all’ basis. In Main and Nebraska, ‘congressional district method’ was used. one elector was elected in each congressional district by popular votes, and the other two electors are selected statewide by popular voting.
There are debates about electoral college. Some people say that there are constraints with electoral college, others argue that there are proponents despite the constraints. According to the article ‘the ELectoral College’, the constraints of Electoral Colleges are
- the possibility of electing a minority president
- the risk of so-called "faithless" Electors,
- the possible role of the Electoral College in depressing voter turnout, and
- its failure to accurately reflect the national popular will.
Meanwhile, it has proponents are
- contributes to the cohesiveness of the country by requiring a distribution of popular support to be elected president
- enhances the status of minority interests,
- contributes to the political stability of the nation by encouraging a two-party system, and
- maintains a federal system of government and representation.
Presidents elected against popular votes in United States
Although the electoral college system is a solid lasting compromise, it is not perfect. One major issue is that the winning candidate may not be winning the most popular votes. This happens several times in the history. The following cases show more details:
| Year 1824 | Presidential Candidates | Electoral votes | Popular votes |
| |
John Quincy Adams (won) | 84 | 113,122 |
| |
Andrew Jackson | 91 | 151,271 |
| |
William H. Crawford |
41 |
41,032 |
| |
Henry Clay |
37 |
47,545 |
- This is an rare case: even though Jackson earned the most electoral and popular votes, he failed to receive more than half of the electoral votes. The House of Representative chose Adams as the president. Candidate Adam won without being voted by most citizens.
| Year 1876 |
Presidential Candidates |
Electoral votes |
Popular votes |
| |
Rutherford B. Hayes (won) |
185 |
4,034,311 |
| |
Samuel Tilden |
184 |
4,288,546 |
| Year 1888 | Presidential Candidates | Electoral votes | Popular votes |
| |
Benjamin Harrison (won) | 233 | 5,443,892 |
| |
Grover Cleveland | 168 | 5,534,488 |
| |
Clinton Fisk |
0 |
250,017 |
| |
Alson Streeter |
0 |
149,115 |
| Year 2000 | Presidential Candidates | Electoral votes | Popular votes |
| |
George W. Bush (won) | 271 | 50,456,002 |
| |
Al Gore | 266 | 50,999,897 |
| |
Ralph Nader |
0 |
2,882,955 |
| |
Pat Buchanan |
0 |
448,895 |
| |
Harry Browne |
0 |
384,431 |
- The above three cases have one thing in common: the winning candidate earned the most electoral votes while another candidate earned more popular votes.
Electoral votes versus Popular votes
National popular voting plan
National popular voting is as introduced before, an alternative way to vote the president while guaranteeing the winner of election (etc, the President) received the most popular votes in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. It can be more clearly told by its own website:
"The National Popular Vote bill would guarantee the Presidency to the candidate who receives the most popular votes in the entire United States. The bill preserves the Electoral College, while ensuring that every vote in every state will matter in every presidential election."
National popular voting plan (NPV) is started in purposing of making every vote same. It’s based on two state powers established in U.S. Constitution: states have plenary power to decide how to apportion their electoral votes and the states have the power to enter into binding interstate compacts. It has been introduced by state legislators in all 50 states and District of Columbia in December 2010. To join this plan, the legislators have to pass National Popular Vote Bill and signed it into law.
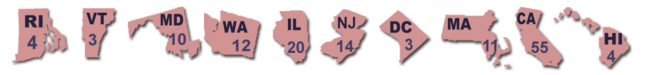
Currently, NPV is the most popular voting method candidate with the most supports to replace electoral votes. It is now proposed and waiting for votes. To make this proposal into effect, it needs 270 or more electoral votes to agree this system. As the latest news, Rhode Island Governor Lincoln Chafee signs National Popular Vote bill in July 2013. And after that, there are 10 jurisdictions possessing 136 electoral votes (50.4% of the 270 electoral votes) in total joining this plan. Besides, at least one legislative chamber in 21 states (including AR, CO, CT, DE, ME, MI, NV, NM, NY, NC, and OR) have passed this bill. There are 2124 state legislators have endorsed the bill.
- 10 jurisdictions signed the National popular Vote bill into law
| Jurisdiction | Electoral Votes | Passed time |
| District of Columbia | 3 | September 21, 2010 |
| Hawaii | 4 | May 1, 2008 |
| Illinois | 20 | April 7, 2008 |
| Maryland | 10 | April 10, 2007 |
| Massachusetts | 11 | August 4, 2010 |
| New Jersey | 14 | January 13, 2008 |
| Washington | 12 | May 6, 2009 |
| Vermont | 3 | April 22, 2011 |
| California | 55 | August 8, 2011 |
| Rhode Island | 4 | July 12, 2013 |
Pros and Cons
The pros and cons of NPV are still under discussion. Same as its current support rate, not all people think this is better than current voting system -- electoral votes, though it may caused the “unwilling” candidate becomes the president.
Supporters of NPV claim that this voting system will, obviously, give a fairer result. This can intuitively present the supporting rate of all candidates, and never let a candidate who lost the popular vote win as it original purpose. Meanwhile, they argued that the candidates put too much emphasis on large swing states and therefore negating smaller states under electoral votes system.
However, critics give different comments. They believe that NPV will discourage candidates from campaigning and paying attention to sparsely populated regions of the country. This will lead the problem that the rural America is neglected and densely populated cities, for example, are focused too intently.
Conclusion
...
Reference:
Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indirect_election
Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_election
United States Constitution: http://2008election.procon.org/sourcefiles/USConstitution.pdf
The Electoral College: http://uselectionatlas.org/INFORMATION/INFORMATION/electcollege_procon.php
President election history: http://2008election.procon.org/view.resource.php?resourceID=001565
National Popular Vote Bill has passed half-way point: http://www.nationalpopularvote.com/
About.com US politics: http://uspolitics.about.com/od/electionissues/a/3-Ways-To-Bypass-The-Electoral-College.htm