| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:ECE637]] | [[Category:ECE637]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:slecture]] |
[[Category:image processing]] | [[Category:image processing]] | ||
[[Category:lecture notes]] | [[Category:lecture notes]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
</font size> | </font size> | ||
| − | A | + | A [[slectures|slecture]] by [[user:Mhossain | Maliha Hossain]] |
<font size= 3> Subtopic 1: Intro to Optical Imaging Systems </font size> | <font size= 3> Subtopic 1: Intro to Optical Imaging Systems </font size> | ||
Revision as of 08:36, 19 June 2013
The Bouman Lectures on Image Processing
A slecture by Maliha Hossain
Subtopic 1: Intro to Optical Imaging Systems
© 2013
Contents
Excerpt from Prof. Bouman's Lecture
Accompanying Lecture Notes
SLR and DSLR Cameras
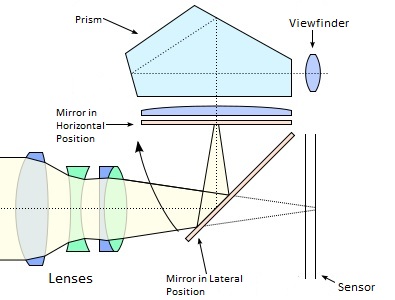
This portion of the lecture provides an overview of digital imaging systems, digital cameras and lenses. Images are typically captured via optical imaging systems, particularly cameras. The figure below describes the mechanism behind how an image is captured in a Single Length Reflex (SLR) camera.
As you point your camera at an object and look through the viewfinder, light from the object passes through the lens and is incident on the mirror, which is positioned laterally so as to reflect the light through the prism and into the viewfinder. Once you click to take a picture, the aperture closes and the mirror moves to the horizontal position shown in the figure. Next, the aperture reopens for the amount of time specified by the mode you have your camera set to. This time the light passing through the lens is incident upon the light sensor. In a DSLR camera, the information from the sensor is digitized and stored in local memory. Once this is completed, the mirror moves back to the lateral position and you can view objects through the viewfinder again.
The key item in the design of a camera is the lens and it is important to characterize the imaging system. You can find the notes on these two topics in the links provided below.
References
- C. A. Bouman. ECE 637. Class Lecture. Digital Image Processing I. Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Purdue University. Spring 2013.
Questions and comments
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them on this page
Back to the "Bouman Lectures on Image Processing" by Maliha Hossain