| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
General theory of nth order ODE: | General theory of nth order ODE: | ||
| + | |||
An nth order linear differential equation is an equation of the form | An nth order linear differential equation is an equation of the form | ||
[[Image:Equation1.png]] | [[Image:Equation1.png]] | ||
Revision as of 22:26, 10 March 2013
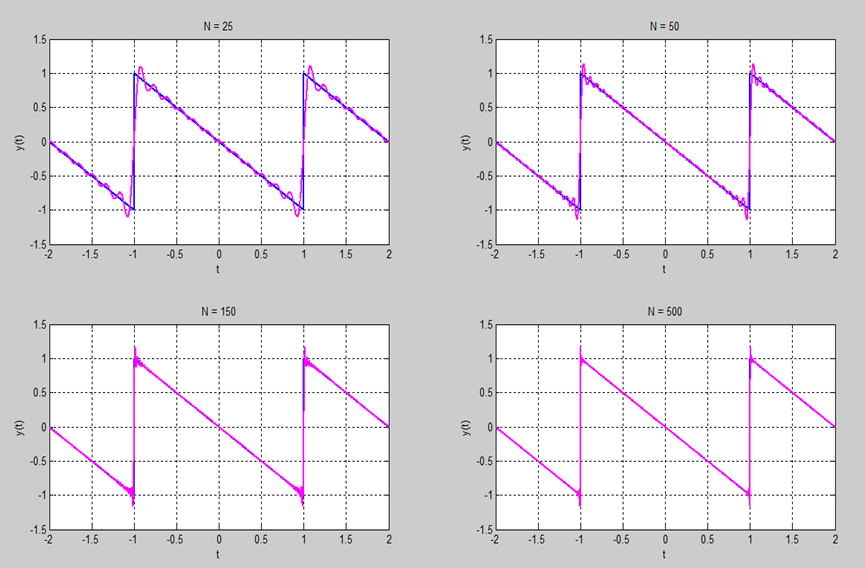
An impulse response, often denoted by h(t), is also called a transfer function or frequency response in frequency domain. It’s the output of In a LTI system when presented with a impulse signal input δ(t). In a LTI systems, impulse response is also equivalent to green’s function used in physics.
General theory of nth order ODE:
An nth order linear differential equation is an equation of the form
![]()
Divide by Po(t) to get the following form
Has n initial conditions
A theorem states, if the functions p1, p2 …..,pn, and G are continuous on the open interval I, then there exists exactly one solution y = φ(t) of the differential equation (2) that also satisfies the initial conditions (3).
Source: Elementary differential eqution with boundary value problems by William E boyce. Ricahrd DeDrima