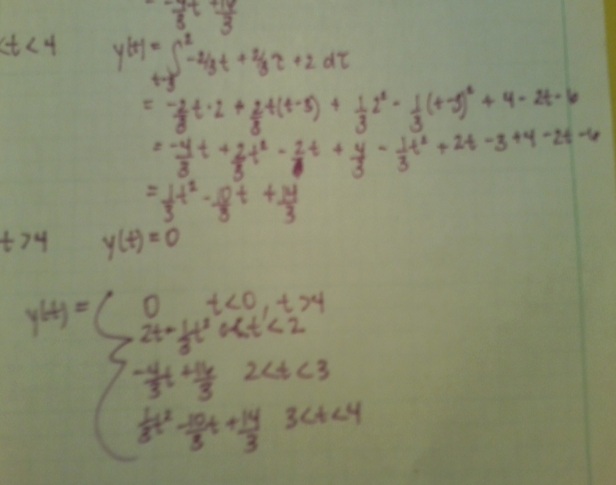(New page: Category:ECE301Spring2013JVK Category:ECE Category:ECE301 Category:probability Category:problem solving EXTRA CREDIT 1. Category:LTI systems Linear and Non Linear ...) |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
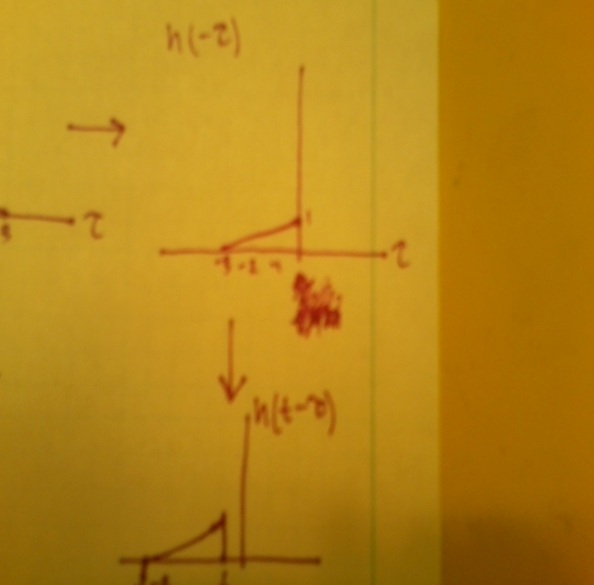
2. [[Category:convolution]] | 2. [[Category:convolution]] | ||
| − | + | Part 1:[[Image:Convol_1.jpg]] | |
| + | Part 2:[[Image:Convol_2.jpg]] | ||
| + | Part 3:[[Image:Convol_3.jpg]] | ||
| + | Part 4:[[Image:Convol_4.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 15:33, 10 February 2013
EXTRA CREDIT 1. Linear and Non Linear
Linear example $ y[n] = 54x[n] $, $ h[n] = 62x[n] $, $ y[n] + h[n] = 54x[n] + 62x[n] $ Non Linear example $ y(t) =x^3(t) $, $ h(t) = x^3(t) $, $ y(t) + h(t) = (x(t)+x(t))^2 $ =\= $ x^2(t) +x^2(t) $
Causal and Non Causal
Causal example $ y[n]=70x[n-1] $ Non Causal example $ y[n]=76x[n+1] $
Memory and Memoryless
Memory example $ y[n]=x[n]+x[n-1] $ Memoryless example $ y[n]=36x[n] $
Invertible and noninvertible
Invertible example $ y(t)=5x(t) $ Nonivertible example $ y(t)=x^4(t) $
Stable and Nonstable
Stable example $ y(t)=sin(3t) $ Nonstable example $ y(t)=4e^3x(t) $
Time variant and Time invariant
Time variant example $ y(t)=3tx(t) $
Time Invariant example $ y(t)=3x(t) $
2.