| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
The Fourier series coefficients for <math>x[n]</math> are: | The Fourier series coefficients for <math>x[n]</math> are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font size="4.5"> | ||
| + | <math>a_{0} = 1</math> | ||
| + | </font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a_{1} = -\frac{1}{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font size="4.5"> | ||
| + | <math>a_{2} = 0</math> | ||
| + | </font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a_{3} = -\frac{1}{2}</math> | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 23 September 2008
Contents
DT LTI System
$ y[n] = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}\frac{1}{2}x[n] \; \; $ (scaled DT integral)
h[n]
$ h[n] = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}\frac{1}{2}\delta [n] = \frac{1}{2}u[n] $
H(z)
$ H(z) = \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty}h[m] e^{-j \omega m} = \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{1}{2}u[m] e^{-j \omega m} = \sum_{m=0}^{\infty} \frac{1}{2}e^{-j \omega m} = \sum_{m=0}^{\infty} (\frac{1}{2 e^{j \omega}})^m = \frac{1}{1-\frac{1}{2 e^{j \omega}}} $ (geometric series $ r^n $ where $ |r| < 1 $)
Response to x[n]
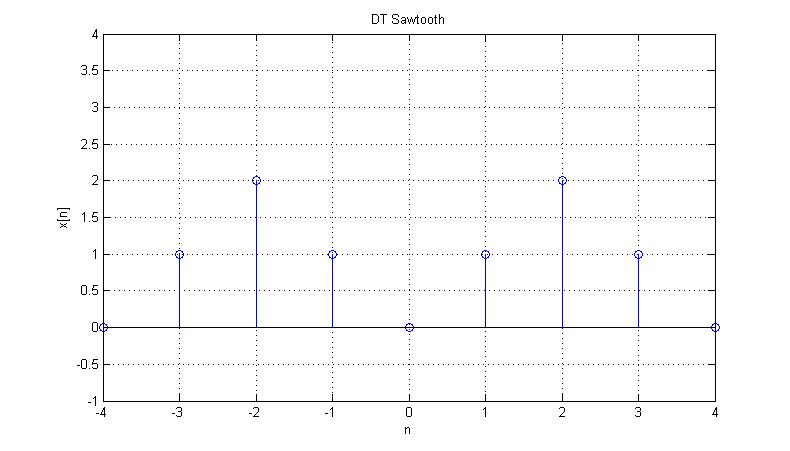
Input $ x[n] $ is the following signal:
The Fourier series coefficients for $ x[n] $ are:
$ a_{0} = 1 $
$ a_{1} = -\frac{1}{2} $
$ a_{2} = 0 $
$ a_{3} = -\frac{1}{2} $