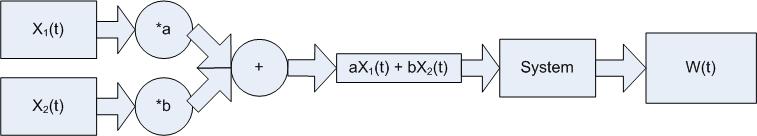(→Examples) |
(→Examples) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Linear: | Linear: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Non-Linear: | Non-Linear: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 17:49, 11 September 2008
Definition
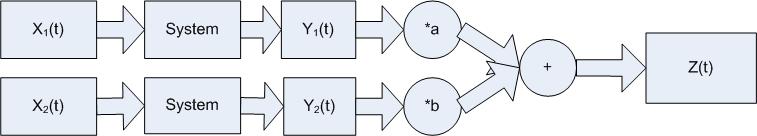
If Z(t) and W(t) in the following are equal the system is linear.
Examples
Linear:
Non-Linear: