(→Non Periodic Signal) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Non Periodic Signal== | ==Non Periodic Signal== | ||
| − | Sampling every t = | + | Sampling every t = 2 |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Samp2_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
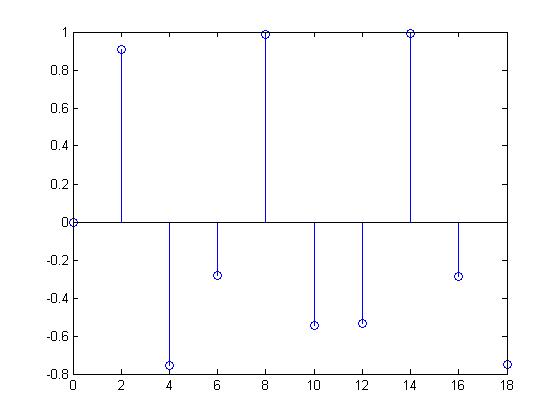
| + | For this discrete time signal which was produced by sampling the same sine wave at a frequency of 0.5, the values of x[n] are non-periodic because <math>x[n + k] \neq x[n]</math> | ||
==2. Create a periodic signal by summing shifted copies of a non-periodic signal== | ==2. Create a periodic signal by summing shifted copies of a non-periodic signal== | ||
Revision as of 08:02, 11 September 2008
Contents
1. Creating two DT signals (one periodic and one non-periodic) from a periodic CT signal
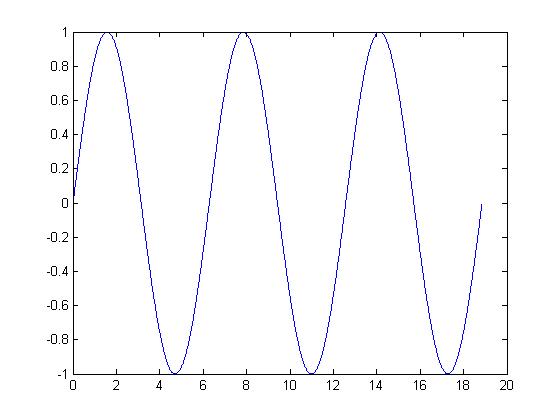
Let x(t) = sin (t), which is a periodic CT signal
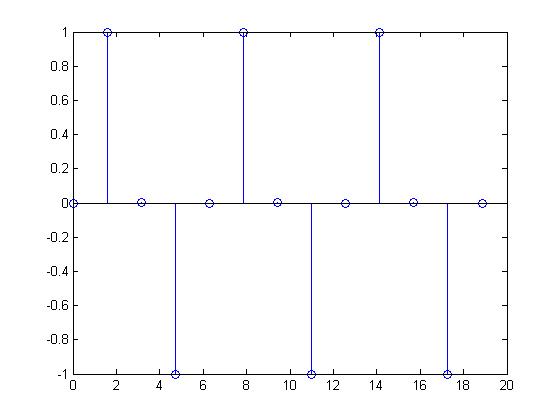
Periodic Signal
This discrete time signal was produced from a CT sine wave by sampling at a frequency of $ \frac{1}{\pi} $.
As can be seen from the graph, the values of x[n] are periodic because they repeat after every period of $ t = 2\pi $.
Therefore, $ x[n + 2\pi] = x[n] $
Non Periodic Signal
For this discrete time signal which was produced by sampling the same sine wave at a frequency of 0.5, the values of x[n] are non-periodic because $ x[n + k] \neq x[n] $