| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
similar for 1-j: <math>180^{\circ} - 45^{\circ} - 18.43^{\circ} + 90^{\circ} = -153.43^{\circ}</math> | similar for 1-j: <math>180^{\circ} - 45^{\circ} - 18.43^{\circ} + 90^{\circ} = -153.43^{\circ}</math> | ||
| − | C) <math> s^2 \; K+1 \;\;\; 2K </math> | + | C) <math> s^2 \; K+1 \;\;\;\;\; 2K </math> |
<math> s^1 \; 2-2K</math> | <math> s^1 \; 2-2K</math> | ||
<math>s^0 \; -2K </math> | <math>s^0 \; -2K </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | set <math>2-2K = 0 \Rightarrow K =1</math>, so system stable at <math>0<K<1</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | when <math>K=1</math>, for <math>s^2</math> row, <math>2s^2+2 = 0 \Rightarrow \omega_n = 1</math> | ||
==Problem 4== | ==Problem 4== | ||
Revision as of 22:45, 1 August 2019
Automatic Control (AC)
Question 1: Feedback Control Systems
August 2017 (Published in Jul 2019)
Contents
Problem 1
A) $ \frac{C(s)}{R(s)} = \frac{4}{s(s+1)} $
B) $ \frac{B(s)}{E(s)} = \frac{2}{s+1}+\frac{4}{s(s+1)} = \frac{2s+4}{s(s+1)} $
C) $ \frac{C(s)}{R(s)} = \frac{\frac{4}{s(s+1)}}{1+\frac{2s+4}{s(s+1)}} $
D) $ 1+\frac{2s+4}{s(s+1)} = 0 $
E) $ s(s+1)+2s+4 = 0 \Rightarrow s^2+3s+4=0 $
$ \therefore \omega_n^2 =4, \; 2\zeta \omega_n = 3 \Rightarrow \tau = \frac{1}{\zeta \omega_n} = \frac{3}{2} $
F) $ \frac{3}{4} $
G) since $ \zeta > 0 \therefore \omega_n = 2 $
H) two poles, type 2
I) $ \ddot{y}(t)+\dot{y}(t) = 4u(t) $
Problem 2
$ k_p = \lim_{s\rightarrow 0} G(s) = \infty $
$ k_v = \lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sG(s) = \frac{K}{6} $
$ e_ss = \lim_{s\rightarrow 0}sE(s) = \lim_{s\rightarrow 0} \frac{sR(s)}{1+G(s)} = \frac{1}{1+\lim_{s\rightarrow 0}G(s)} + \frac{1}{\lim_{s\rightarrow 0}sG(s)} = \frac{1}{1+k_p} + \frac{1}{k_v} = 0.2 $ $ \therefore K = 30 $
Problem 3
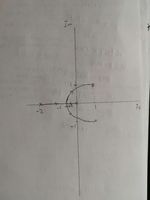
B) Two complex conjugate zeros:
arrival angle of zero 1+j:
angle to zeros: $ (1+j) - (1-j) = 90^{\circ} $
angle to poles: $ (1+j) - 0 = 45^{\circ} $
$ (1+j) - (-2) = 3+j = 18.43^{\circ} $
Arrival angle of 1+j: $ 180^{\circ} + 45^{\circ} + 18.43^{\circ} - 90^{\circ} = 153.43^{\circ} $
similar for 1-j: $ 180^{\circ} - 45^{\circ} - 18.43^{\circ} + 90^{\circ} = -153.43^{\circ} $
C) $ s^2 \; K+1 \;\;\;\;\; 2K $
$ s^1 \; 2-2K $
$ s^0 \; -2K $
set $ 2-2K = 0 \Rightarrow K =1 $, so system stable at $ 0<K<1 $
when $ K=1 $, for $ s^2 $ row, $ 2s^2+2 = 0 \Rightarrow \omega_n = 1 $