| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
2. Time scaling- In simple terms you are shifting the height/width of the graph of a signal. | 2. Time scaling- In simple terms you are shifting the height/width of the graph of a signal. | ||
[[File:Graph1.2.PNG|amplitude scaling graph example]] | [[File:Graph1.2.PNG|amplitude scaling graph example]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The change in graph depends on the value of a. If |a|>0, then the height increases, else it decreases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Time reversal- | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Graph1.3.PNG|time reversal]] | ||
Revision as of 19:56, 1 December 2018
Time dependent changes-
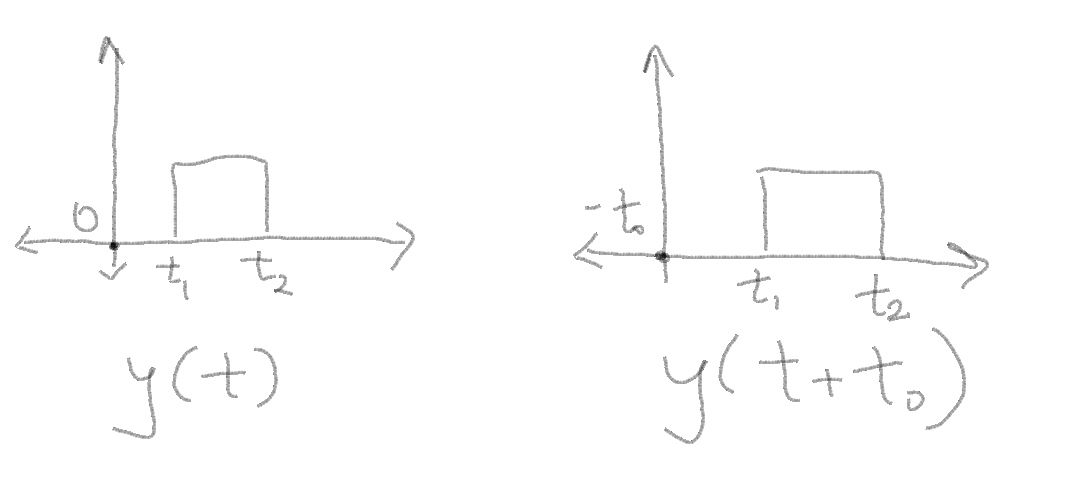
1. Time delay- In simple terms you are shifting the original signal by a factor. For eg.
In this example as you can see, a simple way of understanding time shift/delay is by looking at how the graph changes when you want a shift in the signal.
2. Time scaling- In simple terms you are shifting the height/width of the graph of a signal.
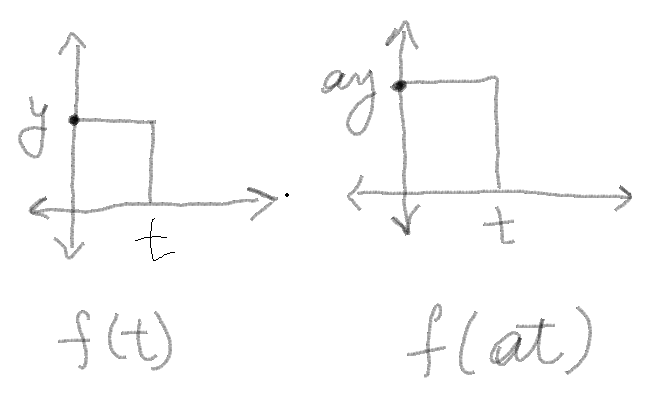
The change in graph depends on the value of a. If |a|>0, then the height increases, else it decreases.
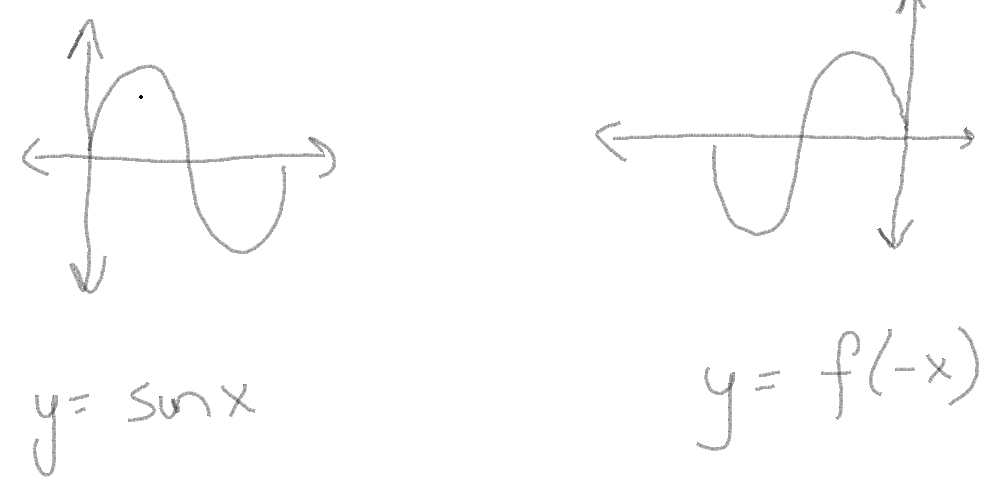
3. Time reversal-