| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Vector derivatives provide a concise way to express vector equations in a way independent of the particular coordinate system being used, while making underlying physics more apparent. Compare, for example, the Navier-Stokes equations in vector form: | Vector derivatives provide a concise way to express vector equations in a way independent of the particular coordinate system being used, while making underlying physics more apparent. Compare, for example, the Navier-Stokes equations in vector form: | ||
| − | <math>\frac{\partial \rho \vec{u}}{\partial t} + \left(\vec{u}\cdot\nabla\right)\vec{u} = -\nabla P + \nabla\cdot(\mu\nabla\vec{u})</math> | + | <math>\frac{\partial \rho \vec{u}}{\partial t} + \left(\vec{u}\cdot\nabla\right)\rho\vec{u} = -\nabla P + \nabla\cdot(\mu\nabla\vec{u})</math> |
With the Navier-Stokes equations in terms of partial derivatives in Cartesian coordinates | With the Navier-Stokes equations in terms of partial derivatives in Cartesian coordinates | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
This tutorial will make use of several [[VectorFormulas | vector derivative identities]]. In particular, these: | This tutorial will make use of several [[VectorFormulas | vector derivative identities]]. In particular, these: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\nabla\cdot(\phi\vec{v}) = \nabla\phi\cdot\vec{v} + \phi \nabla\cdot\vec{u}</math> | ||
| + | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | ==Gradient in Cylindrical Coordinates== | ||
| + | To obtain an expression for the gradient operator in cylindrical coordinates, start with the multivariate chain rule: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} = \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial r} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial r} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial r}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} = \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial \theta} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial \theta} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial \theta}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} = \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial z} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial z} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial z}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In matrix form: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \frac{\partial x}{\partial r} & \frac{\partial y}{\partial r} & \frac{\partial z}{\partial r} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial x}{\partial \theta} & \frac{\partial y}{\partial \theta} & \frac{\partial z}{\partial \theta} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial x}{\partial z} & \frac{\partial y}{\partial z} & \frac{\partial z}{\partial z} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\end{bmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The entries of the square matrix come from the coordinate transformation itself: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x = r \cos \theta \rightarrow \frac{\partial x}{\partial r} = \cos \theta \text{ , } \frac{\partial x}{\partial \theta} = -r\sin \theta</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>y = r \sin \theta \rightarrow \frac{\partial y}{\partial r} = \sin \theta \text{ , } \frac{\partial y}{\partial \theta} = r\cos \theta</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>z = z \rightarrow \frac{\partial x}{\partial z} = \frac{\partial y}{\partial z} = 0 \text{ , } \frac{\partial z}{\partial z} = 1</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \cos \theta & \sin \theta & 0 \\ | ||
| + | -r \sin\theta & r \cos\theta & 0 \\ | ||
| + | 0 & 0 & 1\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} | ||
| + | \end{bmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This gives the partial derivatives with respect to cylindrical coordinate variables in terms of partial derivatives with respect to Cartesian coordinate variables. We can go the other way by inverting this linear system: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \cos \theta & -\frac{\sin \theta}{r} & 0 \\ | ||
| + | \sin \theta & \frac{\cos\theta}{r} & 0 \\ | ||
| + | 0 & 0 & 1\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} \\ | ||
| + | \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} | ||
| + | \end{bmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We are now ready to tackle the gradient in cylindrical coordinates | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 19:51, 12 March 2013
Contents
Divergence and Gradient Theorems
by Kilian Cooley
INTRODUCTION
Vector derivatives provide a concise way to express vector equations in a way independent of the particular coordinate system being used, while making underlying physics more apparent. Compare, for example, the Navier-Stokes equations in vector form:
$ \frac{\partial \rho \vec{u}}{\partial t} + \left(\vec{u}\cdot\nabla\right)\rho\vec{u} = -\nabla P + \nabla\cdot(\mu\nabla\vec{u}) $
With the Navier-Stokes equations in terms of partial derivatives in Cartesian coordinates
$ \frac{\partial \rho u}{\partial t} + u\frac{\partial u}{\partial x} + v\frac{\partial u}{\partial y} + w\frac{\partial u}{\partial z} = -\frac{\partial P}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x}(\mu \frac{\partial u}{\partial x}) + \frac{\partial}{\partial y}(\mu \frac{\partial u}{\partial y}) + \frac{\partial}{\partial z}(\mu \frac{\partial u}{\partial z}) $
$ \frac{\partial \rho v}{\partial t} + u\frac{\partial v}{\partial x} + v\frac{\partial v}{\partial y} + w\frac{\partial v}{\partial z} = -\frac{\partial P}{\partial y} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x}(\mu \frac{\partial v}{\partial x}) + \frac{\partial}{\partial y}(\mu \frac{\partial v}{\partial y}) + \frac{\partial}{\partial z}(\mu \frac{\partial v}{\partial z}) $
$ \frac{\partial \rho w}{\partial t} + u\frac{\partial w}{\partial x} + v\frac{\partial w}{\partial y} + w\frac{\partial w}{\partial z} = -\frac{\partial P}{\partial z} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x}(\mu \frac{\partial w}{\partial x}) + \frac{\partial}{\partial y}(\mu \frac{\partial w}{\partial y}) + \frac{\partial}{\partial z}(\mu \frac{\partial w}{\partial z}) $
The subtle point is that although the latter three equations would appear different if written in cylindrical coordinates (the partial derivatives in $ x, y, z $ would be replaced with ones in $ r,\theta,z $), the vector equation does not. However, the implementations of the operators gradient and divergence do depend on the coordinate system.
In Cartesian coordinates, gradient and divergence are defined as below, where $ n $ is the number of spatial dimensions involved. If $ x_1, x_2, ..., x_n $ are the coordinate directions and
$ \hat{e}_i , i = 1,2,...,n $
are the unit vectors in those directions, then
$ \nabla\cdot\vec{v} = \sum_{i=1}^n \frac{\partial v_i}{\partial x_i} \text{, where } \vec{v} = \sum_{i=1}^n v_i \hat{e}_i $
$ \nabla\phi = \sum_{i=1}^n \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x_i} \hat{e}_i $
Based on this definition, one might expect that in cylindrical coordinates, the gradient operation would be
$ \nabla\phi \neq \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r}\hat{e}_r + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta}\hat{e}_{\theta} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\hat{e}_z $
By simply taking the partial derivatives of $ \phi $ with respect to each coordinate direction, multiplying each derivative by the corresponding unit vector, and adding the resulting components together. This is actually not correct for coordinate systems other than Cartesian. One could arrive at the correct formula for the gradient by performing some tedious changes of variables, and repeat the process for the other vector derivatives. However that approach has many opportunities for error and does not produce much insight as to why the coefficients of the partial derivatives are what they are. This tutorial shows a different way to arrive at the same results but with less calculation.
Preliminaries
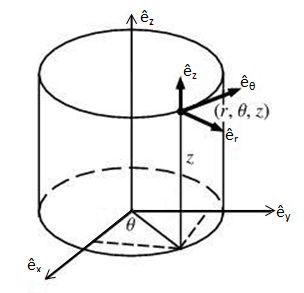
This tutorial will denote vector quantities with an arrow atop a letter, except unit vectors that define coordinate systems which will have a hat. 3-D Cartesian coordinates will be indicated by $ x, y, z $ and cylindrical coordinates with $ r,\theta,z $.
This tutorial will make use of several vector derivative identities. In particular, these:
$ \nabla\cdot(\phi\vec{v}) = \nabla\phi\cdot\vec{v} + \phi \nabla\cdot\vec{u} $
Gradient in Cylindrical Coordinates
To obtain an expression for the gradient operator in cylindrical coordinates, start with the multivariate chain rule:
$ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} = \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial r} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial r} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial r} $
$ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} = \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial \theta} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial \theta} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial \theta} $
$ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} = \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial z} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial z} + \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial z} $
In matrix form:
$ \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial x}{\partial r} & \frac{\partial y}{\partial r} & \frac{\partial z}{\partial r} \\ \frac{\partial x}{\partial \theta} & \frac{\partial y}{\partial \theta} & \frac{\partial z}{\partial \theta} \\ \frac{\partial x}{\partial z} & \frac{\partial y}{\partial z} & \frac{\partial z}{\partial z} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\end{bmatrix} $
The entries of the square matrix come from the coordinate transformation itself:
$ x = r \cos \theta \rightarrow \frac{\partial x}{\partial r} = \cos \theta \text{ , } \frac{\partial x}{\partial \theta} = -r\sin \theta $
$ y = r \sin \theta \rightarrow \frac{\partial y}{\partial r} = \sin \theta \text{ , } \frac{\partial y}{\partial \theta} = r\cos \theta $
$ z = z \rightarrow \frac{\partial x}{\partial z} = \frac{\partial y}{\partial z} = 0 \text{ , } \frac{\partial z}{\partial z} = 1 $
$ \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \cos \theta & \sin \theta & 0 \\ -r \sin\theta & r \cos\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} \end{bmatrix} $
This gives the partial derivatives with respect to cylindrical coordinate variables in terms of partial derivatives with respect to Cartesian coordinate variables. We can go the other way by inverting this linear system:
$ \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \cos \theta & -\frac{\sin \theta}{r} & 0 \\ \sin \theta & \frac{\cos\theta}{r} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} \\ \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} \end{bmatrix} $
We are now ready to tackle the gradient in cylindrical coordinates
References
$ \int_0^1\int_0^4\int_{-1}^7\nabla\phi {dV} = \frac{\partial u}{\partial x}\hat{e}_x $
$ \iiint_{\partial \Omega} {\mathbb R} $