m (ECE PhD QE CNSIP Jan 2000 Problem1.1 moved to ECE PhD QE CNSIP Jan 2001 Problem1.1: wrong year!) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Category:problem solving]] | [[Category:problem solving]] | ||
[[Category:random variables]] | [[Category:random variables]] | ||
| + | [[Category:probability]] | ||
| − | = | + | <center> |
| + | <font size= 4> | ||
| + | [[ECE_PhD_Qualifying_Exams|ECE Ph.D. Qualifying Exam]] | ||
| + | </font size> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font size= 4> | ||
| + | Communication, Networking, Signal and Image Processing (CS) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Question 1: Probability and Random Processes | ||
| + | </font size> | ||
| + | |||
| + | January 2001 | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | =Part 1= | ||
State and prove the Tchebycheff Inequality. | State and prove the Tchebycheff Inequality. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 09:36, 13 September 2013
Communication, Networking, Signal and Image Processing (CS)
Question 1: Probability and Random Processes
January 2001
Contents
Part 1
State and prove the Tchebycheff Inequality.
Solution 1 (retrived from here)
First we state the Chebyshev Inequality: Let $ \mathbf{X} $ be a random variable with mean $ \mu $ and variance $ \sigma^{2} $ . Then $ \forall\epsilon>0 $
$ p\left(\left\{ \left|\mathbf{X}-\mu\right|\geq\epsilon\right\} \right)\leq\frac{\sigma^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}} $.
Now we prove it.
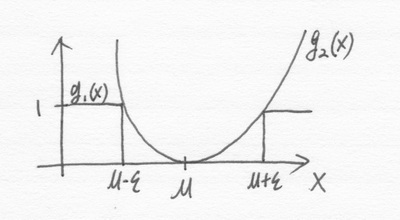
$ \text{Let }g_{1}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)=\mathbf{1}_{\left\{ r\in\mathbf{R}:\left|\mathbf{X}-\mu\right|\geq\epsilon\right\} }\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\text{ and }g_{2}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)=\frac{\left(\mathbf{X}-\mu\right)^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}} $.
$ \text{Let }\phi\left(\mathbf{X}\right)=g_{2}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)-g_{1}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\Longrightarrow\phi\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\geq0,\;\forall\mathbf{X}\in\mathbf{R}. $
$ E\left[\phi\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\right]=E\left[g_{2}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)-g_{1}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\right]=E\left[g_{2}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\right]-E\left[g_{1}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\right]=\frac{\sigma^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}}-p\left(\left\{ \left|\mathbf{X}-\mu\right|\geq\epsilon\right\} \right)\text{ and }E\left[\phi\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\right]\geq0. $
$ \because E\left[g_{2}\left(\mathbf{X}\right)\right]=E\left[\frac{\left(\mathbf{X}-\mu\right)^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}}\right]=\frac{1}{\epsilon^{2}}E\left[\left(\mathbf{X}-\mu\right)^{2}\right]=\frac{\sigma^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}}. $
$ \therefore p\left(\left\{ \left|\mathbf{X}-\mu\right|\geq\epsilon\right\} \right)\leq\frac{\sigma^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}}. $
Solution 2 (retrived from here)
$ E\left[\mathbf{X}\right]=\int_{0}^{\epsilon}xf_{\mathbf{X}}\left(x\right)dx+\int_{\epsilon}^{\infty}xf_{\mathbf{X}}\left(x\right)dx\geq\int_{\epsilon}^{\infty}xf_{\mathbf{X}}\left(x\right)dx\geq\int_{\epsilon}^{\infty}\epsilon f_{\mathbf{X}}\left(x\right)dx=\epsilon P\left(\left\{ \mathbf{X}\geq\epsilon\right\} \right). $
$ P\left(\left\{ \mathbf{X}\geq\epsilon\right\} \right)\leq\frac{E\left[\mathbf{X}\right]}{\epsilon}. $
$ P\left(\left\{ \left|\mathbf{X}-\mu\right|\geq\epsilon\right\} \right)=P\left(\left\{ \left(\mathbf{X}-\mu\right)^{2}\geq\epsilon^{2}\right\} \right)\leq\frac{E\left[\left(\mathbf{X}-\mu\right)^{2}\right]}{\epsilon^{2}}=\frac{\sigma^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}}. $
$ \therefore p\left(\left\{ \left|\mathbf{X}-\mu\right|\geq\epsilon\right\} \right)\leq\frac{\sigma^{2}}{\epsilon^{2}}. $
Solution 3
Write it here.