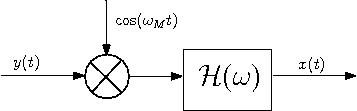| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
:<math>5+\mathcal{R}e\{s\}>0</math> | :<math>5+\mathcal{R}e\{s\}>0</math> | ||
:<math>\mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-5</math> | :<math>\mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-5</math> | ||
| + | <span style="color:red"> This is an example where the ROC appears "like magic" at the end. Four points should be taken off for this. In order to get full credit, you must specify at which point the equality fails to hold in your computation of the Fourier transform. For example, like this: </span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | X(s)&=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-5t}u(t+3)e^{-st} dt \\ | ||
| + | &=\int_{-3}^{\infty}e^{-(5+s)t} dt \\ | ||
| + | &=-\frac{1}{s+5}e^{-(5+s)t}\Bigg|^{\infty}_{-3} \\ | ||
| + | &=\left\{ | ||
| + | \begin{array}{ll} | ||
| + | \frac{e^{3(5+s)}}{s+5},& \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-5\\ | ||
| + | diverges, & \text{ else.} | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right. | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
b) | b) | ||
| Line 141: | Line 155: | ||
&=\int_{-\infty}^{5}e^{-(5+s)t} dt \\ | &=\int_{-\infty}^{5}e^{-(5+s)t} dt \\ | ||
&=-\frac{1}{s+5}e^{-(5+s)t}\Bigg|_{-\infty}^{5} \\ | &=-\frac{1}{s+5}e^{-(5+s)t}\Bigg|_{-\infty}^{5} \\ | ||
| − | &=-\frac{e^{-5(5+s)}}{s+5} | + | &=\left\{ |
| + | \begin{array}{ll} | ||
| + | -\frac{e^{-5(5+s)}}{s+5}& \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}<-5\\ | ||
| + | diverges, & \text{ else.} | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right. | ||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
c) | c) | ||
| Line 169: | Line 184: | ||
&=\int_{-\infty}^{0}e^{2t}e^{-st}dt + \int_{0}^{\infty}e^{-2t}e^{-st}dt \\ | &=\int_{-\infty}^{0}e^{2t}e^{-st}dt + \int_{0}^{\infty}e^{-2t}e^{-st}dt \\ | ||
&=\int_{-\infty}^{0}e^{(2-s)t}dt + \int_{0}^{\infty}e^{-(2+s)t}dt \\ | &=\int_{-\infty}^{0}e^{(2-s)t}dt + \int_{0}^{\infty}e^{-(2+s)t}dt \\ | ||
| − | &=\frac{1}{2-s}e^{(2-s)t}\Bigg|^{0}_{-\infty}-\frac{1}{2+s}e^{-(2+s)t}\Bigg|_{0}^{\infty} \\ | + | &=\frac{1}{2-s}e^{(2-s)t}\Bigg|^{0}_{-\infty}-\frac{1}{2+s}e^{-(2+s)t}\Bigg|_{0}^{\infty} |
| − | &=\frac{1}{2-s}+\frac{1}{2+s} | + | \end{align} |
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now consider the first term: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | \frac{1}{2-s}e^{(2-s)t}\Bigg|^{0}_{-\infty} &= | ||
| + | \left\{ | ||
| + | \begin{array}{ll} | ||
| + | \frac{1}{2-s} & \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}<2\\ | ||
| + | diverges, & \text{ else.} | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right. | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | So the ROC for this first term is <math class="inline">\mathcal{R}e\{s\}<2</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now consider the second term: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | -\frac{1}{2+s}e^{-(2+s)t}\Bigg|_{0}^{\infty}&= | ||
| + | \left\{ | ||
| + | \begin{array}{ll} | ||
| + | \frac{1}{2+s} & \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-2\\ | ||
| + | diverges, & \text{ else.} | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right. | ||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | + | So the ROC for this second term is <math class="inline">\mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-2</math>. | |
| − | Thus the ROC is the intersection of those two constraints and hence ROC is <math class="inline">-2<\mathcal{R}e\{s\}<2</math>. | + | Thus the ROC for the sum of both terms is the intersection of those two constraints, and hence the ROC is <math class="inline">-2<\mathcal{R}e\{s\}<2</math>. |
Revision as of 16:08, 17 April 2011
Contents
Homework 10 Solutions, ECE301 Spring 2011 Prof. Boutin
Students should feel free to make comments/corrections or ask questions directly on this page.
Question 1
a) We can write
- $ y_1(t)=e^{j \theta_c}x(t)e^{j\omega_c t} $
Notice that this is exactly as modulating by $ e^{j\omega_c t} $ but now we are multiplying with a complex exponential independent of $ t $ (phase shift). We can recover the signal $ x(t) $ for any $ \omega_c $, and hence there are no conditions put on $ \omega_c $.
b) In order to recover signal $ x(t) $, we multiply $ y_1(t) $ by $ e^{-j(\omega_c+\theta_c)} $.
c) We can write
- $ y_2(t)=x(t)\left(\frac{e^{j\omega_c t}-e^{-j\omega_c t}}{2j}\right) $
Taking the FT of $ y_2(t) $, we get:
- $ \begin{align} \mathcal{Y}_2(\omega)&=\frac{1}{2\pi(2j)}\mathcal{X}(\omega)*[2\pi\delta(\omega-\omega_c)-2\pi\delta(\omega+\omega_c)] \\ &=\frac{1}{2j}\mathcal{X}(\omega-\omega_c)-\frac{1}{2j}\mathcal{X}(\omega+\omega_c) \end{align} $
Now, to insure that we can recover signal $ x(t) $ we need to avoid having the two images of $ X(\omega) $ overlap. Hence we need $ \omega_c>\omega_M $. But $ \omega_M=2000\pi/2=1000\pi $. Hence in order for $ x(t) $ to be recoverable we need:
- $ \omega_c>1000\pi $
d) In order to recover signal $ x(t) $ we multiply $ y_2(t) $ by $ \sin(\omega_c t) $ first. The signal after multiplying with $ \sin(\omega_c t) $ is:
- $ \begin{align} r(t)&=y_2(t)\sin(\omega_c t) \\ &=\sin^2(\omega_c t)x(t) \\ &=\frac{1}{2}x(t)-\frac{1}{2}\cos(2\omega_c t)x(t) \end{align} $
Thus in order to recover $ x(t) $ we need to filter out the second term of $ r(t) $ and amplify the remainder by a factor of 2 (you may want to draw the FT of $ r(t) $ to verify this in the frequency domain). To achieve that, we pass $ r(t) $ through a low pass filter with a cut-off frequency $ \omega_{cut}=\omega_M=1000\pi $ and gain 2. The frequency response of this low pass filter is:
- $ \mathcal{H}(\omega)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 2, & \mbox{ for } |\omega|<1000\pi\\ 0, & \mbox{ elsewhere} \end{array}\right. $
Note that the cut-off frequency of the low pass filter can actually be anywhere between $ \omega_M $ and $ 2\omega_c-\omega_M $.
Question 2
a) The Fourier series coefficients of $ c(t) $ are:
- $ \begin{align} a_k&=\frac{\sin(\frac{2\pi k 10^{-3}}{4\times 10^{-3}})}{\pi k} \\ &=\frac{\sin{\frac{\pi k}{2}}}{\pi k} \end{align} $
and using the synthesis equation of the Fourier series we get:
- $ c(t)=\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} a_k e^{j\frac{2\pi k}{T}t}=\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} a_k e^{j2000\pi kt} $
Taking the FT of the latter sum, we get:
- $ \mathcal{C}(\omega)=2\pi\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}a_k \delta(\omega-2000\pi k) $
Now, let $ y(t)=x(t)c(t) $, then:
$ \begin{align} \mathcal{Y}(\omega)&=\frac{1}{2\pi}\mathcal{X}(\omega)*\mathcal{C}(\omega) \\ &=\frac{1}{2\pi}\mathcal{X}(\omega)*2\pi\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}a_k \delta(\omega-2000\pi k) \\ &=\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}a_k \mathcal{X}(\omega-2000\pi k) \end{align} $
In order to recover $ x(t) $ we need to avoid aliasing and hence $ 2000\pi>2\omega_M $. Then $ \omega_M<1000\pi $.
b) We need to find $ a_0 $ since the image at DC is multiplied by it:
- $ a_0=\lim_{k\to 0}\frac{\sin{\frac{\pi k}{2}}}{\pi k}=\frac{\frac{\pi k}{2}}{\pi k}=\frac{1}{2} $
Now, to recover $ x(t) $ we need to filter out the images other than the image at DC and and multiply it by $ \frac{1}{a_0}=2 $. Hence we use a low pass filter with the following frequency response:
- $ \mathcal{H}(\omega)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 2, & \mbox{ for } |\omega|<\omega_{M}\\ 0, & \mbox{ elsewhere} \end{array}\right. $
Note that the cut-off frequency of the low pass filter can actually be anywhere between $ \omega_M $ and $ 2000\pi-\omega_M $.
Question 3
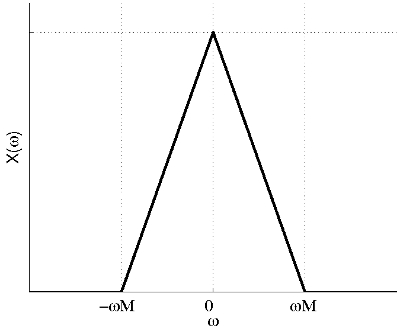
a) We can assume any illustrative shape for the spectrum of signal $ x(t) $ as long as it is band-limited between $ -\omega_M $ and $ \omega_M $.
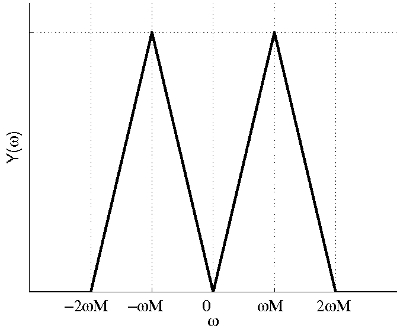
Thus the spectrum of $ y(t) $ is:
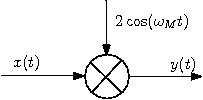
b) A block diagram of the scrambler that can generate the signal $ y(t) $ can be:
You can verify that by taking the FT of $ 2x(t)\cos(\omega_M t) $.
c) The following block diagram describes a descrambler which can recover signal $ x(t) $ from $ y(t) $.
where $ \mathcal{H}(\omega)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1, & \mbox{ for } |\omega|<\omega_M\\ 0, & \mbox{ elsewhere} \end{array}\right. $.
Note that $ \mathcal{H}(\omega) $ is the frequency response of a low pass filter with cut-off frequency equals to $ \omega_M $.
You can verify that the system in the above block diagram can recover signal $ x(t) $ by following the same reasoning of part d) in Question 1.
Question 4
a)
$ \begin{align} X(s)&=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-5t}u(t+3)e^{-st} dt \\ &=\int_{-3}^{\infty}e^{-(5+s)t} dt \\ &=-\frac{1}{s+5}e^{-(5+s)t}\Bigg|^{\infty}_{-3} \\ &=\frac{e^{3(5+s)}}{s+5} \end{align} $
where the ROC is:
- $ \mathcal{R}e\{5+s\}>0 $
- $ 5+\mathcal{R}e\{s\}>0 $
- $ \mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-5 $
This is an example where the ROC appears "like magic" at the end. Four points should be taken off for this. In order to get full credit, you must specify at which point the equality fails to hold in your computation of the Fourier transform. For example, like this:
$ \begin{align} X(s)&=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-5t}u(t+3)e^{-st} dt \\ &=\int_{-3}^{\infty}e^{-(5+s)t} dt \\ &=-\frac{1}{s+5}e^{-(5+s)t}\Bigg|^{\infty}_{-3} \\ &=\left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \frac{e^{3(5+s)}}{s+5},& \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-5\\ diverges, & \text{ else.} \end{array} \right. \end{align} $
b)
$ \begin{align} X(s)&=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-5t}u(-t+5)e^{-st} dt \\ &=\int_{-\infty}^{5}e^{-(5+s)t} dt \\ &=-\frac{1}{s+5}e^{-(5+s)t}\Bigg|_{-\infty}^{5} \\ &=\left\{ \begin{array}{ll} -\frac{e^{-5(5+s)}}{s+5}& \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}<-5\\ diverges, & \text{ else.} \end{array} \right. \end{align} $
c)
$ \begin{align} X(s)&=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-5t}[u(t)-u(t-3)]e^{-st} dt \\ &=\int_{0}^{3}e^{-(5+s)t} dt \\ &=-\frac{1}{s+5}[e^{-3(5+s)}-1]\\ &=\frac{1}{s+5}-\frac{e^{-3(5+s)}}{s+5} \end{align} $
where we did not need to constraint our result to a ROC (which is expected since the signal has finite duration).
d)
$ \begin{align} X(s)&=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-2|t|}e^{-st}dt \\ &=\int_{-\infty}^{0}e^{2t}e^{-st}dt + \int_{0}^{\infty}e^{-2t}e^{-st}dt \\ &=\int_{-\infty}^{0}e^{(2-s)t}dt + \int_{0}^{\infty}e^{-(2+s)t}dt \\ &=\frac{1}{2-s}e^{(2-s)t}\Bigg|^{0}_{-\infty}-\frac{1}{2+s}e^{-(2+s)t}\Bigg|_{0}^{\infty} \end{align} $
Now consider the first term:
$ \begin{align} \frac{1}{2-s}e^{(2-s)t}\Bigg|^{0}_{-\infty} &= \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \frac{1}{2-s} & \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}<2\\ diverges, & \text{ else.} \end{array} \right. \end{align} $
So the ROC for this first term is $ \mathcal{R}e\{s\}<2 $.
Now consider the second term:
$ \begin{align} -\frac{1}{2+s}e^{-(2+s)t}\Bigg|_{0}^{\infty}&= \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \frac{1}{2+s} & \text{ if } \mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-2\\ diverges, & \text{ else.} \end{array} \right. \end{align} $
So the ROC for this second term is $ \mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-2 $.
Thus the ROC for the sum of both terms is the intersection of those two constraints, and hence the ROC is $ -2<\mathcal{R}e\{s\}<2 $.
Question 5
Since the Laplace transform of $ x(t) $ has exactly two poles at $ s=-1 $ and $ s=-3 $, then the ROC could be any of the following three:
- $ \mathcal{R}e\{s\}<-1 $
- $ \mathcal{R}e\{s\}<-3 $
- $ -3<\mathcal{R}e\{s\}<-1 $
But it is given that the FT of $ e^{2t}x(t) $ converges and hence $ s=-2 $ belongs to the ROC of the Laplace transform of $ x(t) $.
Hence the ROC is $ -3<\mathcal{R}e\{s\}<-1 $.
Since the ROC is $ -3<\mathcal{R}e\{s\}<-1 $, we deduce that the given signal is a sum of a right-sided signal and a left-sided signal. Thus, $ x(t) $ should be a two-sided signal.
Hence:
a) No
b) No
c) Yes
Question 6
In order to find the inverse Laplace transform of $ X(s) $, we need to find its partial fraction expansion.
First we compute the roots of the denominator, and then we get:
- $ X(s)=\frac{2(s+2)}{s^2+7s+12}=\frac{2(s+2)}{(s+3)(s+4)} $
Now we write:
- $ X(s)=\frac{A}{s+3}+\frac{B}{s+4} $
Multiplying both sides by $ (s+3)(s+4) $ and simplifying, we get:
- $ 2s+4=(A+B)s+4A+3B $
Comparing and solving, we have that: $ A=-2 $ and $ B=4 $.
Thus,
- $ X(s)=-\frac{2}{s+3}+\frac{4}{s+4} $
Now since the ROC is $ \mathcal{R}e\{s\}>-3 $, then $ x(t) $ should be a right sided signal or equivalently the sum of right sided signals. Hence,
- $ x(t)=[-2e^{-3t}+4e^{-4t}]u(t) $