m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<object width="425" height="355"><param name="movie" value="http://www.youtube.com/v/wzJkaATyitA&hl=en"></param><param name="wmode" value="transparent"></param><embed src="http://www.youtube.com/v/wzJkaATyitA&hl=en" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" wmode="transparent" width="425" height="355"></embed></object> | <object width="425" height="355"><param name="movie" value="http://www.youtube.com/v/wzJkaATyitA&hl=en"></param><param name="wmode" value="transparent"></param><embed src="http://www.youtube.com/v/wzJkaATyitA&hl=en" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" wmode="transparent" width="425" height="355"></embed></object> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:BayesYouTubeLink_Old Kiwi.jpg]] | ||
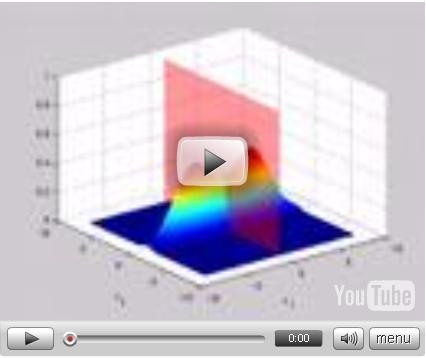
The video demonstrates Bayes decision rule on 2D feature data from two classes. We visualize the decision hyper surface as a red "wall" cutting through the bi-modal distribution of the data, and observe how it changes with the parameters of the Gaussian distributions for the two classes. Note that if the covariance matrices and the priors of the classes are identical, then the decision surface cuts directly between the two modes. If the prior of one class increases, the decision surface is "pushed away" from that mode, biasing the classifier in favor of the more likely class. | The video demonstrates Bayes decision rule on 2D feature data from two classes. We visualize the decision hyper surface as a red "wall" cutting through the bi-modal distribution of the data, and observe how it changes with the parameters of the Gaussian distributions for the two classes. Note that if the covariance matrices and the priors of the classes are identical, then the decision surface cuts directly between the two modes. If the prior of one class increases, the decision surface is "pushed away" from that mode, biasing the classifier in favor of the more likely class. | ||
Revision as of 09:40, 7 April 2008
<object width="425" height="355"><param name="movie" value="http://www.youtube.com/v/wzJkaATyitA&hl=en"></param><param name="wmode" value="transparent"></param><embed src="http://www.youtube.com/v/wzJkaATyitA&hl=en" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" wmode="transparent" width="425" height="355"></embed></object>
The video demonstrates Bayes decision rule on 2D feature data from two classes. We visualize the decision hyper surface as a red "wall" cutting through the bi-modal distribution of the data, and observe how it changes with the parameters of the Gaussian distributions for the two classes. Note that if the covariance matrices and the priors of the classes are identical, then the decision surface cuts directly between the two modes. If the prior of one class increases, the decision surface is "pushed away" from that mode, biasing the classifier in favor of the more likely class.
The code for making such a video is here: Media:BayesDecisionSurface.tar.gz_Old Kiwi
For more on Bayes' decision rule, see Lecture 6_Old Kiwi