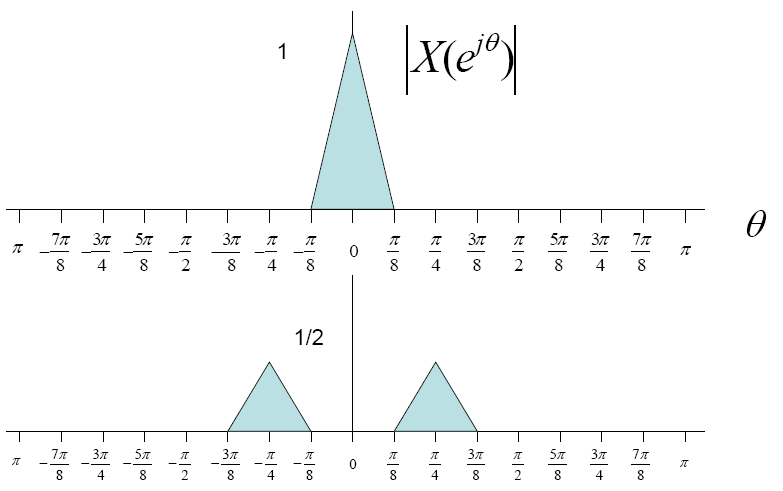(→AM Demodulation) |
(→AM Demodulation) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
<math>Y(e^{j\theta})= R(e^{j\theta})H(e^{j\theta})</math><br> | <math>Y(e^{j\theta})= R(e^{j\theta})H(e^{j\theta})</math><br> | ||
| − | <math> = [\frac{1}{2}X(e^{j\theta})+\frac{1}{4}X(e^{j\theta-2\phi})+\frac{1}{4}X(e^{j\theta+2\phi})]H(e^{j\theta}</math><br> | + | <math> = [\frac{1}{2}X(e^{j\theta})+\frac{1}{4}X(e^{j\theta-2\phi})+\frac{1}{4}X(e^{j\theta+2\phi})]H(e^{j\theta})</math><br> |
<math> = X(e^{j\theta}) </math> | <math> = X(e^{j\theta}) </math> | ||
[[Image:hw91_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | [[Image:hw91_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | ||
[[Image:hw92_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | [[Image:hw92_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:48, 17 November 2008
AM modulation
Now we know that
$ x(t) $ ⇒ $ X(\omega) $
Now suppose the input signal was multiplied by a cosine wave
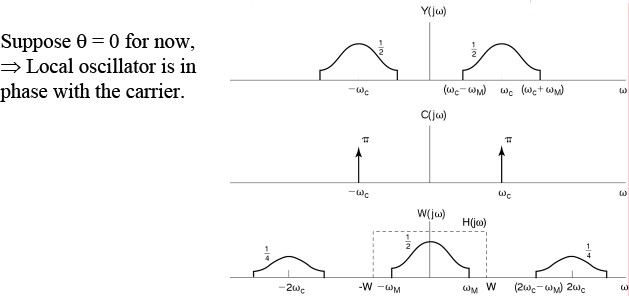
then the fourier transform of the wave would look as follows
$ x(t)*cos(\frac{\pi t}{4}) $ ⇒ $ \frac{1}{2}[X(e^{j(\theta - \pi/4)}) + X(e^{j(\theta + \pi/4)}) ] $.
In short we are getting two side bands which look something like this
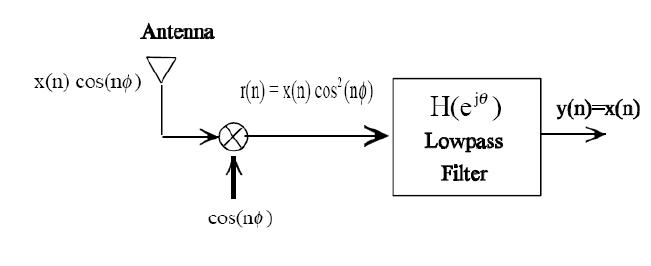
AM Demodulation
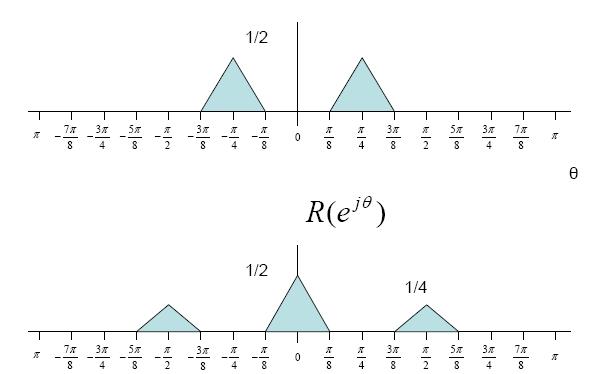
$ r(n)= x(n)cos^2(n \theta)= \frac{1}{2} x(n) + \frac{1}{2}x(n)cos(2n\theta) $
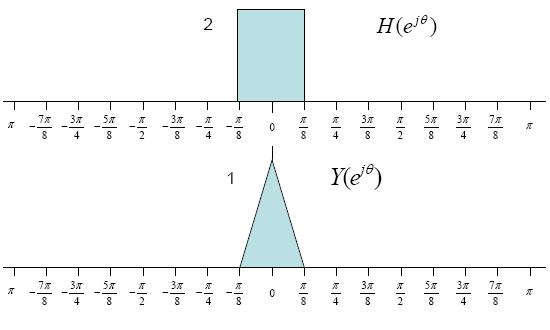
$ Y(e^{j\theta})= R(e^{j\theta})H(e^{j\theta}) $
$ = [\frac{1}{2}X(e^{j\theta})+\frac{1}{4}X(e^{j\theta-2\phi})+\frac{1}{4}X(e^{j\theta+2\phi})]H(e^{j\theta}) $
$ = X(e^{j\theta}) $