| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Periodic CT Signal and Its Fourier Coefficients == | == Periodic CT Signal and Its Fourier Coefficients == | ||
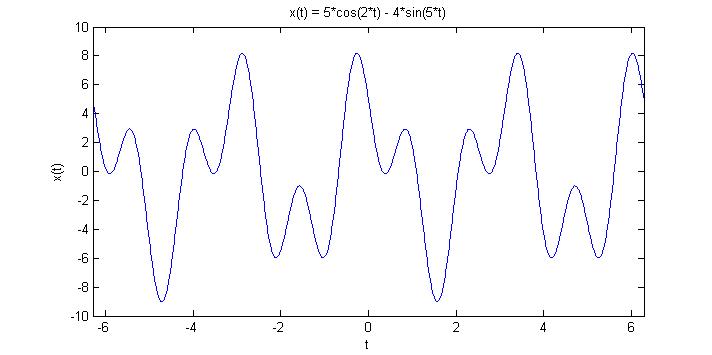
| − | Take the signal <math> x(t) = 5cos(2t) - 4sin( | + | Take the signal <math> x(t) = 5cos(2t) - 4sin(5t) </math>. The graph below proves that it is indeed periodic, with a period <math> T = \pi </math>. |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:ECE301HW4p1_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] |
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Therefore, | Therefore, | ||
| − | <math> x(t) = 5 * \frac{1}{2} * (e</math><sup>(j2t)</sup> <math> \,\ + e</math><sup>(-j2t)</sup><math> \,\ ) - 4 * \frac{1}{ | + | <math> x(t) = 5 * \frac{1}{2} * (e</math><sup>(j2t)</sup> <math> \,\ + e</math><sup>(-j2t)</sup><math> \,\ ) - 4 * \frac{1}{5j} * (e</math><sup>(j5t)</sup> <math> \,\ - e</math><sup>(-j5t)</sup><math> \,\ )</math> |
| − | The period <math> \,\ T = \pi </math> so if <math> \,\ w_0 = \frac{2\pi}{T} </math>, then <math> \,\ w_0 = | + | The period <math> \,\ T = 2\pi </math> so if <math> \,\ w_0 = \frac{2\pi}{T} </math>, then <math> \,\ w_0 = 1 </math>. |
Revision as of 13:43, 25 September 2008
Periodic CT Signal and Its Fourier Coefficients
Take the signal $ x(t) = 5cos(2t) - 4sin(5t) $. The graph below proves that it is indeed periodic, with a period $ T = \pi $.
$ \,\ sin(x) = \frac{1}{2j} * (e $(jx) $ \,\ - e $(-jx)$ \,\ ) $
and
$ \,\ cos(x) = \frac{1}{2} * (e $(jx) $ \,\ + e $(-jx)$ \,\ ) $
Therefore,
$ x(t) = 5 * \frac{1}{2} * (e $(j2t) $ \,\ + e $(-j2t)$ \,\ ) - 4 * \frac{1}{5j} * (e $(j5t) $ \,\ - e $(-j5t)$ \,\ ) $
The period $ \,\ T = 2\pi $ so if $ \,\ w_0 = \frac{2\pi}{T} $, then $ \,\ w_0 = 1 $.