m |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Background of Population= | =Background of Population= | ||
---- | ---- | ||
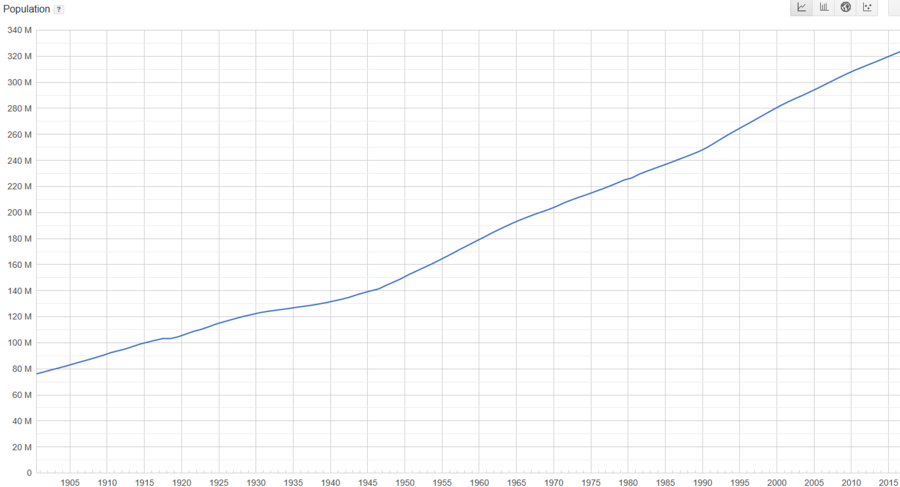
| − | In order to have a better sense of how the US population has grown, here is a graph | + | In order to have a better sense of how the US population has grown, here is a graph based on the official data from the government website: https://www.census.gov. |
<center>[[File:77777.png|900px|left]]</center> | <center>[[File:77777.png|900px|left]]</center> | ||
<center> <small>''Figure 1 The U.S. population from 1900 to 2018. Adapted from Google.''</small></center> | <center> <small>''Figure 1 The U.S. population from 1900 to 2018. Adapted from Google.''</small></center> | ||
| − | The above image shows the trend of the US population (U.S. Population, 2018). The x-axis indicates the year, and the y-axis shows the size | + | The above image shows the trend of the US population (U.S. Population, 2018). The x-axis indicates the year, and the y-axis shows the US population size. It is easy to notice the population change with time from a large scale. For instance, between 1915 and 1920, it had some fluctuation while the overall size was increasing. |
| − | The | + | The US population size is determined by birth rate, death rate, net migration, and other economic and other sociological factors, such as government policy, technology, age, sex distribution, and economic growth. |
| − | The population projection is based on the mathematical models such as exponential models and logistic models. Since each model only considers limited factors | + | The population projection is based on the mathematical models such as exponential models and logistic models. Since each model only considers limited factors, each has its own disadvantages. For instance, the logistic model only considers birth rate, death rate, initial population size, and the carrying capacity of that region. Carrying capacity is the maximum population size an environment can hold. The logistic model, on the other hand, omits some important factors, such as government policies. In general, the logistic model provides more precise prediction than the exponential model does, as it includes the carrying capacity of a specific region which is ignored in the exponential one. |
Latest revision as of 21:17, 2 December 2018
Background of Population
In order to have a better sense of how the US population has grown, here is a graph based on the official data from the government website: https://www.census.gov.
The above image shows the trend of the US population (U.S. Population, 2018). The x-axis indicates the year, and the y-axis shows the US population size. It is easy to notice the population change with time from a large scale. For instance, between 1915 and 1920, it had some fluctuation while the overall size was increasing.
The US population size is determined by birth rate, death rate, net migration, and other economic and other sociological factors, such as government policy, technology, age, sex distribution, and economic growth.
The population projection is based on the mathematical models such as exponential models and logistic models. Since each model only considers limited factors, each has its own disadvantages. For instance, the logistic model only considers birth rate, death rate, initial population size, and the carrying capacity of that region. Carrying capacity is the maximum population size an environment can hold. The logistic model, on the other hand, omits some important factors, such as government policies. In general, the logistic model provides more precise prediction than the exponential model does, as it includes the carrying capacity of a specific region which is ignored in the exponential one.