| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
This is the process of varying the properties of a specific waveform, also called the carrier signal, using a modulating signal that contains information that is trying to be transmitted. This allows for the signal to be transmitted over an electronic medium. In the real world modulation is used to send radio signals and other TV signals as well. | This is the process of varying the properties of a specific waveform, also called the carrier signal, using a modulating signal that contains information that is trying to be transmitted. This allows for the signal to be transmitted over an electronic medium. In the real world modulation is used to send radio signals and other TV signals as well. | ||
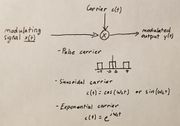
| − | + | Below is the general form for how a signal is modulated. | |
| + | Keep in mind that when there is a specific frequency channel specified, a Bandpass filter must be added at the end of the pulse train example in order to get the proper modulated signal. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Modulation.jpg|thumbnail]] | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Demodulation''' |
| − | + | This is the process of extracting the original information out from the modulated signal. This will allow for a person to grab the proper information from the transmitted modulated signal. | |
| − | + | Below are examples of how to modulate a general signal in terms of sinusoidal, exponential and pulse train. | |
| + | Keep in mind that when there is a specific frequency channel specified, a Bandpass filter must be added in before multiplying by the carrier. | ||
| + | For Pulse Train specifically, a sinusoidal carrier must be multiplied after the bandpass filter and before the low pass filter. | ||
| + | Also, a signal that was shifted to begin with, must be shifted after filtering as well in order to maintain the proper information. | ||
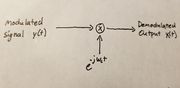
| − | + | '''''Exponential Carrier''' | |
| − | + | [[File:DemodExp.jpg|thumbnail]] | |
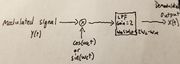
| − | ''''' | + | '''''Sinusoidal Carrier''' |
| + | [[File:DemodCosCos.jpg|thumbnail]] | ||
'''''Pulse-Train Carrier''''' | '''''Pulse-Train Carrier''''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DemodPulse.jpg|thumbnail]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the real world modulation and demodulation is used everywhere. Although not as simple as the above examples, they use the same principle to create signals that can be properly sent. In order to send specific channel information for a specific network, or for a certain radio frequency to be played on a specific channel, it is all done through modulation. Even your Wi-Fi signal is transmitted through a modem. The modem is a modulator and a demodulator in and of itself, hence the name Mo(modulation)Dem(demodulation). As signals are used everywhere in todays world from transmitting music to even sending confidential files securely, a modulation and demodulation technique can be seen in all of them. | ||
Latest revision as of 22:42, 2 December 2018
Summary
The aim of this project is to explain what Modulation and Demodulation are and to show how a signal can be both modulated and demodulated using different methods. I will also attempt to show how these methods are used in real world scenarios
Modulation
This is the process of varying the properties of a specific waveform, also called the carrier signal, using a modulating signal that contains information that is trying to be transmitted. This allows for the signal to be transmitted over an electronic medium. In the real world modulation is used to send radio signals and other TV signals as well.
Below is the general form for how a signal is modulated. Keep in mind that when there is a specific frequency channel specified, a Bandpass filter must be added at the end of the pulse train example in order to get the proper modulated signal.
Demodulation
This is the process of extracting the original information out from the modulated signal. This will allow for a person to grab the proper information from the transmitted modulated signal.
Below are examples of how to modulate a general signal in terms of sinusoidal, exponential and pulse train. Keep in mind that when there is a specific frequency channel specified, a Bandpass filter must be added in before multiplying by the carrier. For Pulse Train specifically, a sinusoidal carrier must be multiplied after the bandpass filter and before the low pass filter. Also, a signal that was shifted to begin with, must be shifted after filtering as well in order to maintain the proper information.
Exponential Carrier
Sinusoidal Carrier
Pulse-Train Carrier
In the real world modulation and demodulation is used everywhere. Although not as simple as the above examples, they use the same principle to create signals that can be properly sent. In order to send specific channel information for a specific network, or for a certain radio frequency to be played on a specific channel, it is all done through modulation. Even your Wi-Fi signal is transmitted through a modem. The modem is a modulator and a demodulator in and of itself, hence the name Mo(modulation)Dem(demodulation). As signals are used everywhere in todays world from transmitting music to even sending confidential files securely, a modulation and demodulation technique can be seen in all of them.