| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:bonus point project]] | ||
=== Linearity === | === Linearity === | ||
Latest revision as of 09:50, 6 May 2012
Linearity
Theory
There are three definitions we discussed in class for linearity.
Definition 1
A system is called linear if for any constants $ a,b\in $ all complex numbers and for any input signals x1(t),x2(t) with response y1(t),y2(t), respectively, the system's response to ax1(t) + bx2(t) is ay1(t) + by2(t).
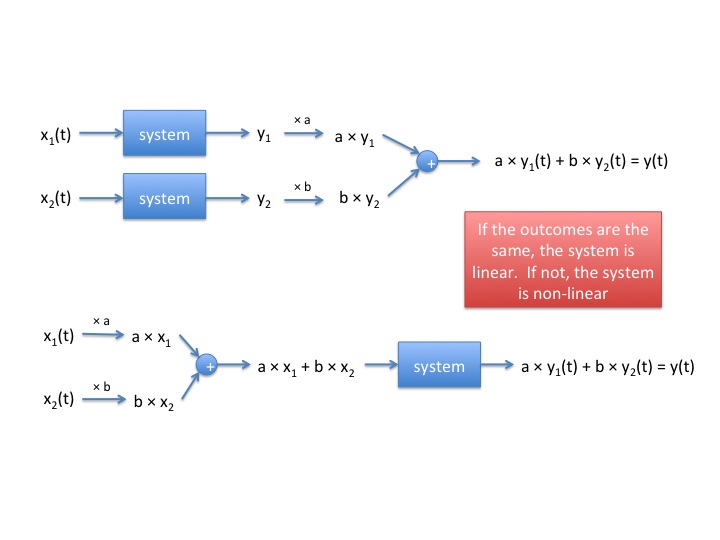
Definition 2
If
$ x_1(t) \rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} system \end{bmatrix} \rightarrow y_1(t) $
$ x_2(t) \rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} system \end{bmatrix} \rightarrow y_2(t) $
then
$ ax_1(t) + bx_2(t) \rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} system \end{bmatrix} \rightarrow ay_1(t) + by_2(t) $
for any $ a,b\in $ all complex numbers, any x1(t),x2(t) then we say the system is linear.
Definition 3
Applications
Linearity can be used to simplify the Fourier transform. Integration and differentiation are also linear. Once a non-linear system is made linear, complex systems are easier to model mathematically. True linear systems are virtually unknown in the real world, but over a small range of variables, systems can be modeled as linear.