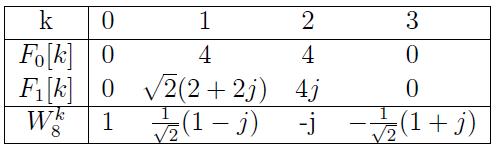| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:Problem_solving]] | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE438]] | ||
| + | [[Category:digital signal processing]] | ||
| + | |||
== Week7 Quiz Pool == | == Week7 Quiz Pool == | ||
| Line 31: | Line 35: | ||
Given the values of <math>X_8[k]</math> for k = 0, 1, ..., 7 determined in Q1, determine the numerical values of <math>k_1\text{ and }k_2</math>. | Given the values of <math>X_8[k]</math> for k = 0, 1, ..., 7 determined in Q1, determine the numerical values of <math>k_1\text{ and }k_2</math>. | ||
| − | |||
Answer [[W7Q2Sol|Here]]. | Answer [[W7Q2Sol|Here]]. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 41: | ||
Q3: | Q3: | ||
| + | Let <math>X_N[k],k=0,...,N-1</math> denote the N point Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the signal x[n],n=0,...,N-1. | ||
| + | For each case below derive an expression for the DFT <math>Y_M[k],k=0,...,M-1</math> of the signal y[n],n=0,...,M-1 in terms of <math>X_N[k],k=0,...,N-1</math> | ||
| − | [[ | + | a. <math>y[n]=e^{j\frac{2\pi}{N}n}x[n],\;\;n=0,...,N-1</math> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | b. <math>y[n]=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}x[N-1], & n=0,\\ x[n-1], & n=1,...,N-1\end{array} \right.</math> | |
| + | c. <math>y[n]=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}x[n/2], & n \text{ is even},\\ 0, & n \text{ is odd},\end{array} \right. n=0,...,2N-1</math> | ||
| − | [[ | + | d. <math>y[n]=x[2n],\;\;n=0,...,N/2-1</math> Assume that N is even. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[W7Q3Sol|Solution]] | ||
---------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | ||
| − | + | Q4: | |
| + | Consider complex signal <math>x[n]=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}e^{j\omega _0 n} & 0\le n\le N-1,\\ 0, & \text{otherwise},\end{array} \right. </math> | ||
| + | a. Compute <math>X(e^{j\omega})</math> the Fourier Transform of x[n]. | ||
| − | [ | + | b. Compute X[k], the N points DFT of x[n]. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | c. For <math>\omega _0=2\pi k_0 /N, </math> where <math>k_0</math> is integer, compute DFT of x[n]. | |
| − | [[ | + | [[W7Q4Sol|Solution]] |
---------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | ||
| + | |||
[[ECE438_Lab_Fall_2010|Back to Lab wiki]] | [[ECE438_Lab_Fall_2010|Back to Lab wiki]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:41, 11 November 2011
Week7 Quiz Pool
Q1: As part of the first stage in a radix 2 FFT, a sequence x[n] of length N = 8 is decomposed into two sequences of length 4 as
$ f_0[n] = x[2n]\text{ , n = 0, 1, 2, 3} $
$ f_1[n] = x[2n + 1]\text{ , n = 0, 1, 2, 3} $
The 4-pt. DFT of each of these two sequences is $ F_0[k]\text{ and }F_1[k] $ respectively.
The specific values of $ F_0[k]\text{ and }F_1[k] $, k = 0, 1, 2, 3, obtained from the length N = 8 sequence in question are listed in the Table below.
From the values of $ F_0[k] \text{ and }F_1[k] $, k = 0, 1, 2, 3, and the values of
$ W_8^k = e^{\frac{-j2\pi k}{8}}, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 $
provided in the Table, determine the numerical values of the actual N = 8-pt. DFT of x[n] denoted $ X_8[k] $ for k = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
Answer Here.
Q2: The underlying length N = 8 sequence of x[n] in Q1 may be expressed as
$ x[n] = e^{j2\pi k_1n/8} + e^{j2\pi k_2n/8}, n = 0,1,2 ..., 7 $
Given the values of $ X_8[k] $ for k = 0, 1, ..., 7 determined in Q1, determine the numerical values of $ k_1\text{ and }k_2 $.
Answer Here.
Q3: Let $ X_N[k],k=0,...,N-1 $ denote the N point Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the signal x[n],n=0,...,N-1.
For each case below derive an expression for the DFT $ Y_M[k],k=0,...,M-1 $ of the signal y[n],n=0,...,M-1 in terms of $ X_N[k],k=0,...,N-1 $
a. $ y[n]=e^{j\frac{2\pi}{N}n}x[n],\;\;n=0,...,N-1 $
b. $ y[n]=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}x[N-1], & n=0,\\ x[n-1], & n=1,...,N-1\end{array} \right. $
c. $ y[n]=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}x[n/2], & n \text{ is even},\\ 0, & n \text{ is odd},\end{array} \right. n=0,...,2N-1 $
d. $ y[n]=x[2n],\;\;n=0,...,N/2-1 $ Assume that N is even.
Q4: Consider complex signal $ x[n]=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}e^{j\omega _0 n} & 0\le n\le N-1,\\ 0, & \text{otherwise},\end{array} \right. $
a. Compute $ X(e^{j\omega}) $ the Fourier Transform of x[n].
b. Compute X[k], the N points DFT of x[n].
c. For $ \omega _0=2\pi k_0 /N, $ where $ k_0 $ is integer, compute DFT of x[n].