(New page: == LECTURE on September 11, 2009 == The perfect reconstruction of '''<math>{x(t)}</math>''' from '''<math>x_s(t)</math>''' is possible if '''<math>X(f) = 0</math>''' when '''<math>|f| \ge...) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== LECTURE on September 11, 2009 == | == LECTURE on September 11, 2009 == | ||
| − | The perfect reconstruction of '''<math>{x(t)}</math>''' from '''<math>x_s(t)</math>''' is possible if '''<math>X(f) = 0</math>''' when '''<math>|f| \ge {1 | + | ---- |
| + | |||
| + | The perfect reconstruction of '''<math> {x(t)}\,\!</math>''' from '''<math>x_s(t)\,\!</math>''' is possible if '''<math>X(f) = 0\,\!</math>''' when '''<math>|f| \ge \frac{1}{|2T|}</math>''' | ||
| + | |||
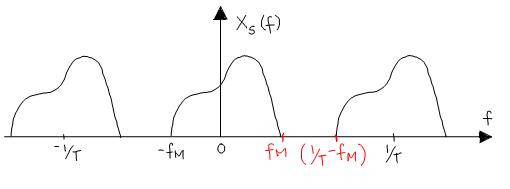
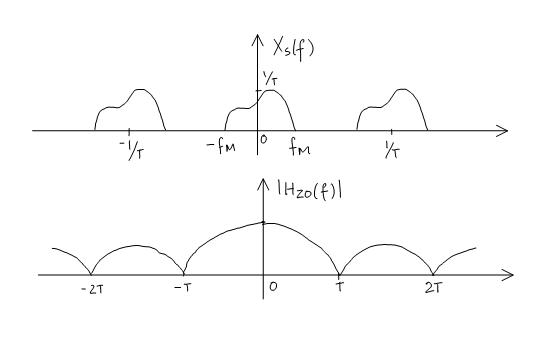
| + | '''PROOF:''' Look at the graph of '''<math>X_s(f)\,\!</math>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ECE438ssuresh1.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To avoid aliasing, | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''<math>\frac{1}{T}\ - f_M \ge f_M</math>''' '''<math>\quad\iff\quad</math>''' '''<math>\frac{1}{T}\ \ge 2f_M</math>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | To recover the signal, we will require a low pass filter with gain '''<math>T\,\!</math>''' and cutoff, '''<math>\frac{1}{2T}</math>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let '''<math>x_r(t)\,\!</math>''' be the reconstructed signal. Then, | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''<math>X_(f) = H_r(f) X_s(f)\,\!</math>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | where, | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''<math>H_r(f) = T rect(f)\,\!</math>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | So, | ||
| + | <div style="margin-left: 3em;"> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \begin{align} | ||
| + | x_r(t) &= h_r(t) * {\color{OliveGreen} X_s(t)} \\ | ||
| + | &= sinc \left (\frac{t}{T}\right) * {\color{Blue} \sum_k X(kT) \delta(t-kT)} \\ | ||
| + | &= \sum_k X(kT) sinc \left (\frac{t}{T}\right) * \delta(t-kT) \\ | ||
| + | &= \sum_k X(kT) sinc \left (\frac{t - kT}{T}\right)\\ | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
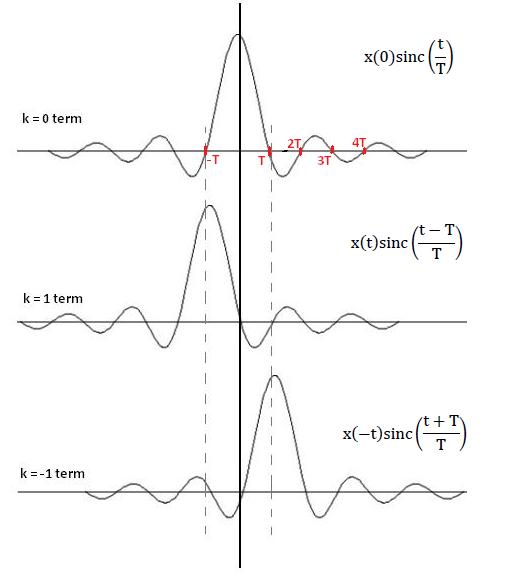
| + | Recall, <math>\quad sinc(x) = 0 \quad \iff \quad x = \pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 3 ... \,\!</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ECE438ssuresh2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | At all integer multiples of T, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x_r(nT) = X(nT)\,\!</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If Nyquist is satisfied, <math>\quad x_r(nT) = X(nT)\quad \forall \quad 't'\,\!</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
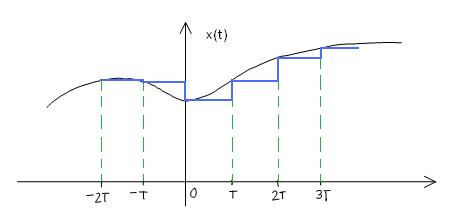
| + | Contrast this reconstruction with the zero-order hold, | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ECE438ssuresh3.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\qquad \Rightarrow piecewise\ construct\ approximation\ </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="margin-left: 3em;"> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \begin{align} | ||
| + | x_r(t) &= \sum_k x(kT)\ rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} - kT}{T}\right) \\ | ||
| + | &= \sum_k x(kT)\ rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * \delta (t - kT)\\ | ||
| + | &= rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * \sum_k x(kT)\ \delta (t - kT) \qquad and\ if\ we\ look\ clearly,\ \\ | ||
| + | &= rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * {\color{Blue}\sum_k x(kT)\ \delta (t - kT)} \\ | ||
| + | &= rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * {\color{OliveGreen} X_s(t)}\\ | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
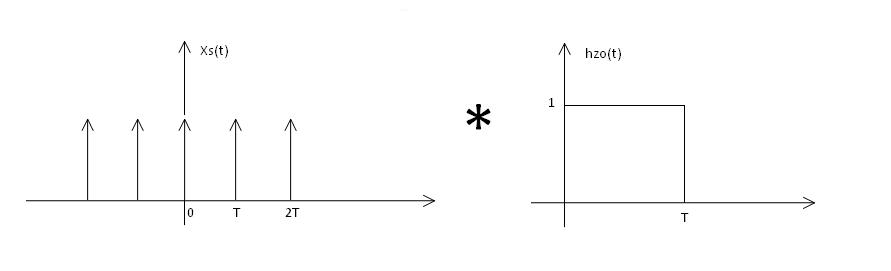
| + | <div style="font-family: Verdana, sans-serif; font-size: 12px; text-align: center; width: 30%; margin: 0px; border: 1px solid #aaa; padding: 1em;"> <math>\therefore\ x_r(t) = h_{zo} (t) * X_s(t)</math> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ECE438ssuresh4.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In the frequency domain, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>X_r(f) = S_s(f) H_{zo}(f) \qquad ; \qquad H_{zo}(f) = T sinc (Tf) e^{ (-j2 \pi fT/T) } </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ECE438ssuresh5.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | So even though <math>x_r(t)\,\!</math> is not band limited, its higher frequency components are attenuated because the <math>|H_{zo}(f)|\ \,\!</math> decreases as <math>|f| </math> increases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | --[[User:Ssuresh|Ssuresh]] 13:47, 23 September 2009 (UTC) | ||
Latest revision as of 09:47, 23 September 2009
LECTURE on September 11, 2009
The perfect reconstruction of $ {x(t)}\,\! $ from $ x_s(t)\,\! $ is possible if $ X(f) = 0\,\! $ when $ |f| \ge \frac{1}{|2T|} $
PROOF: Look at the graph of $ X_s(f)\,\! $
To avoid aliasing,
$ \frac{1}{T}\ - f_M \ge f_M $ $ \quad\iff\quad $ $ \frac{1}{T}\ \ge 2f_M $
To recover the signal, we will require a low pass filter with gain $ T\,\! $ and cutoff, $ \frac{1}{2T} $
Let $ x_r(t)\,\! $ be the reconstructed signal. Then,
$ X_(f) = H_r(f) X_s(f)\,\! $
where,
$ H_r(f) = T rect(f)\,\! $
So,
$ \begin{align} x_r(t) &= h_r(t) * {\color{OliveGreen} X_s(t)} \\ &= sinc \left (\frac{t}{T}\right) * {\color{Blue} \sum_k X(kT) \delta(t-kT)} \\ &= \sum_k X(kT) sinc \left (\frac{t}{T}\right) * \delta(t-kT) \\ &= \sum_k X(kT) sinc \left (\frac{t - kT}{T}\right)\\ \end{align} $
Recall, $ \quad sinc(x) = 0 \quad \iff \quad x = \pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 3 ... \,\! $
At all integer multiples of T,
$ x_r(nT) = X(nT)\,\! $
If Nyquist is satisfied, $ \quad x_r(nT) = X(nT)\quad \forall \quad 't'\,\! $
Contrast this reconstruction with the zero-order hold,
$ \qquad \Rightarrow piecewise\ construct\ approximation\ $
$ \begin{align} x_r(t) &= \sum_k x(kT)\ rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} - kT}{T}\right) \\ &= \sum_k x(kT)\ rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * \delta (t - kT)\\ &= rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * \sum_k x(kT)\ \delta (t - kT) \qquad and\ if\ we\ look\ clearly,\ \\ &= rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * {\color{Blue}\sum_k x(kT)\ \delta (t - kT)} \\ &= rect \left (\frac{t - \tfrac {T}{2} }{T}\right) * {\color{OliveGreen} X_s(t)}\\ \end{align} $
In the frequency domain,
$ X_r(f) = S_s(f) H_{zo}(f) \qquad ; \qquad H_{zo}(f) = T sinc (Tf) e^{ (-j2 \pi fT/T) } $
So even though $ x_r(t)\,\! $ is not band limited, its higher frequency components are attenuated because the $ |H_{zo}(f)|\ \,\! $ decreases as $ |f| $ increases.
--Ssuresh 13:47, 23 September 2009 (UTC)