(New page: == Instructions == Homework 10 can be [https://engineering.purdue.edu/ece302/homeworks/HW10FA08.pdf downloaded here] on the [https://engineering.purdue.edu/ece302/ ECE 302 course website]....) |
|||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 25 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE302Fall2008_ProfSanghavi]] | ||
| + | [[Category:probabilities]] | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE302]] | ||
| + | [[Category:homework]] | ||
| + | [[Category:problem solving]] | ||
| + | |||
== Instructions == | == Instructions == | ||
Homework 10 can be [https://engineering.purdue.edu/ece302/homeworks/HW10FA08.pdf downloaded here] on the [https://engineering.purdue.edu/ece302/ ECE 302 course website]. | Homework 10 can be [https://engineering.purdue.edu/ece302/homeworks/HW10FA08.pdf downloaded here] on the [https://engineering.purdue.edu/ece302/ ECE 302 course website]. | ||
== Problem 1: Random Point, Revisited== | == Problem 1: Random Point, Revisited== | ||
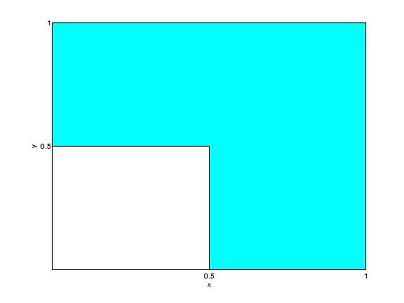
| + | In the following problems, the random point (X , Y) is uniformly distributed on the shaded region shown. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:uniformArea_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *(a) Find the marginal pdf <math>f_X(x)</math> of the random variable <math>X</math>. Find <math>E[X]</math> and <math>Var(X)</math>. | ||
| + | *(b) Using your answer from part (a), find the marginal pdf <math>f_Y(y)</math> of the random variable <math>Y</math>, and its mean and variance, <math>E[Y]</math>, and <math>Var[Y]</math>. | ||
| + | *(c) Find <math>f_{Y|X}(y|\alpha)</math>, the conditional pdf of <math>Y</math> given that <math>X = \alpha</math>, where <math>0 < \alpha < 1/2</math>. Then find the conditional mean and conditional variance of <math>Y</math> given that <math>X = \alpha</math>. | ||
| + | *(d) What is the MMSE estimator, <math>\hat{y}_{\rm MMSE}(x)</math>? | ||
| + | *(e) What is the Linear MMSE estimator, <math>\hat{y}_{\rm LMMSE}(x)</math>? | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 joon young kim_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 Jayanth Athreya_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 (a)&(b) Suan-Aik Yeo_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] (Question by Jonathan, comment by Gregory Pajot) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 (c) Arie Lyles_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] (additional commentary by Brian Thomas) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 (d) Kristin Wing_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] (edited by Nicholas Browdues) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 (a), a much easier way to find fx(x), Chris Rush_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 (e) Spencer Mitchell_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] (question from Nicholas; response by Brian Thomas) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.1 (a) Christopher Wacnik_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
== Problem 2: Variable Dependency== | == Problem 2: Variable Dependency== | ||
| + | Suppose that <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math> are zero-mean jointly Gaussian random variables with variances <math>\sigma_X^2</math> and <math>\sigma_Y^2</math>, respectively and correlation coefficient <math>\rho</math>. | ||
| + | *(a) Find the means and variances of the random variables <math>Z = X\cos\theta + Y\sin\theta</math> and <math>W = Y\cos\theta - X sin\theta</math>. | ||
| + | *(b) What is <math>Cov(Z,W)</math>? | ||
| + | *(c) Find an angle <math>\theta</math> such that <math>Z</math> and <math>W</math> are independent Gaussian random variables. You may express your answer as a trigonometric function involving <math>\sigma_X^2</math>, <math>\sigma_Y^2</math>, and <math>\rho</math>. In particular,what is the value of <math>\theta</math> if <math>\sigma_X = \sigma_Y</math>? | ||
| + | [[10.2 (a&b) Beau Morrison_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.2 Tiffany Sukwanto_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.2 Josh Long_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[10.2 Monsu Mathew_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
== Problem 3: Noisy Measurement== | == Problem 3: Noisy Measurement== | ||
| + | Let <math>X = Y+N</math>, where <math>Y</math> is exponentially distributed with parameter <math>\lambda</math> and <math>N</math> is Gaussian with mean 0 and variance <math>\sigma^2</math>. The variables <math>Y</math> and <math>N</math> are independent, and the parameters <math>\lambda</math> and <math>\sigma^2</math> are strictly positive (Recall that <math>E[Y] = \frac1\lambda</math> and <math>Var(Y) = \frac{1}{\lambda^2}</math>.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Find <math>\hat{Y}_{\rm LMMSE}(X)</math>, the linear minimum mean square error estimator of <math>Y</math> from <math>X</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Hamad Al Shehhi 10.3_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Joe Gutierrez 10.3_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Jaewoo Choi 10.3_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
== Problem 4: Digital Loss== | == Problem 4: Digital Loss== | ||
| + | Let <math>X</math> be a continuous uniform random variable on the interval <math>[0,1]</math>. It is quantized using an <math>n</math>-level quantizer defined as follows: Given an input <math>x</math>, the quantizer outputs a value <math>q(x) = \frac1n\lfloor nx\rfloor</math>; that is, it rounds <math>x</math> down to the nearest multiple of <math>1/n</math>. (Note that for any real number <math>a</math>, <math>\lfloor a\rfloor</math> is the largest integer less than or equal to <math>a</math>). Thus the output of the quantizer is always a value from the set <math>\{0,\frac1n,\frac2n,\ldots,\frac{n-1}n\}</math>. Find the mean-square-error <math>E[(X-q(X))^2]</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Anand Gautam 10.4_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Shao-Fu Shih 10.4_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[AJ Hartnett 10.4_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | [[Justin Mauck 10.4_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi]] | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | [[Main_Page_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi|Back to ECE302 Fall 2008 Prof. Sanghavi]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:58, 22 November 2011
Contents
Instructions
Homework 10 can be downloaded here on the ECE 302 course website.
Problem 1: Random Point, Revisited
In the following problems, the random point (X , Y) is uniformly distributed on the shaded region shown.
- (a) Find the marginal pdf $ f_X(x) $ of the random variable $ X $. Find $ E[X] $ and $ Var(X) $.
- (b) Using your answer from part (a), find the marginal pdf $ f_Y(y) $ of the random variable $ Y $, and its mean and variance, $ E[Y] $, and $ Var[Y] $.
- (c) Find $ f_{Y|X}(y|\alpha) $, the conditional pdf of $ Y $ given that $ X = \alpha $, where $ 0 < \alpha < 1/2 $. Then find the conditional mean and conditional variance of $ Y $ given that $ X = \alpha $.
- (d) What is the MMSE estimator, $ \hat{y}_{\rm MMSE}(x) $?
- (e) What is the Linear MMSE estimator, $ \hat{y}_{\rm LMMSE}(x) $?
10.1 joon young kim_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
10.1 Jayanth Athreya_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
10.1 (a)&(b) Suan-Aik Yeo_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi (Question by Jonathan, comment by Gregory Pajot)
10.1 (c) Arie Lyles_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi (additional commentary by Brian Thomas)
10.1 (d) Kristin Wing_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi (edited by Nicholas Browdues)
10.1 (a), a much easier way to find fx(x), Chris Rush_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
10.1 (e) Spencer Mitchell_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi (question from Nicholas; response by Brian Thomas)
10.1 (a) Christopher Wacnik_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
Problem 2: Variable Dependency
Suppose that $ X $ and $ Y $ are zero-mean jointly Gaussian random variables with variances $ \sigma_X^2 $ and $ \sigma_Y^2 $, respectively and correlation coefficient $ \rho $.
- (a) Find the means and variances of the random variables $ Z = X\cos\theta + Y\sin\theta $ and $ W = Y\cos\theta - X sin\theta $.
- (b) What is $ Cov(Z,W) $?
- (c) Find an angle $ \theta $ such that $ Z $ and $ W $ are independent Gaussian random variables. You may express your answer as a trigonometric function involving $ \sigma_X^2 $, $ \sigma_Y^2 $, and $ \rho $. In particular,what is the value of $ \theta $ if $ \sigma_X = \sigma_Y $?
10.2 (a&b) Beau Morrison_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
10.2 Tiffany Sukwanto_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
10.2 Josh Long_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
10.2 Monsu Mathew_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
Problem 3: Noisy Measurement
Let $ X = Y+N $, where $ Y $ is exponentially distributed with parameter $ \lambda $ and $ N $ is Gaussian with mean 0 and variance $ \sigma^2 $. The variables $ Y $ and $ N $ are independent, and the parameters $ \lambda $ and $ \sigma^2 $ are strictly positive (Recall that $ E[Y] = \frac1\lambda $ and $ Var(Y) = \frac{1}{\lambda^2} $.)
Find $ \hat{Y}_{\rm LMMSE}(X) $, the linear minimum mean square error estimator of $ Y $ from $ X $.
Hamad Al Shehhi 10.3_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
Joe Gutierrez 10.3_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
Jaewoo Choi 10.3_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
Problem 4: Digital Loss
Let $ X $ be a continuous uniform random variable on the interval $ [0,1] $. It is quantized using an $ n $-level quantizer defined as follows: Given an input $ x $, the quantizer outputs a value $ q(x) = \frac1n\lfloor nx\rfloor $; that is, it rounds $ x $ down to the nearest multiple of $ 1/n $. (Note that for any real number $ a $, $ \lfloor a\rfloor $ is the largest integer less than or equal to $ a $). Thus the output of the quantizer is always a value from the set $ \{0,\frac1n,\frac2n,\ldots,\frac{n-1}n\} $. Find the mean-square-error $ E[(X-q(X))^2] $.
Anand Gautam 10.4_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
Shao-Fu Shih 10.4_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi
Justin Mauck 10.4_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi