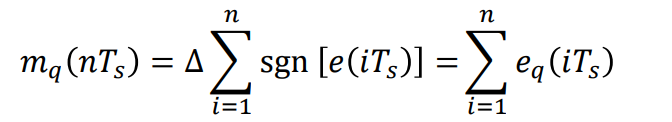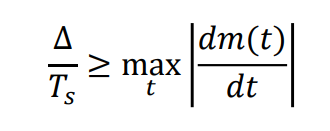| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Data Modulation == | ||
| + | In real life, speakers cannot play signals that are in the digital form. In order to play a sound, a physical voltage must be sent to the speakers. However, most soundtracks are now save in digital form in industry, a DAC, digital-to-analog converter, is needed in virtually every device that can produce a sound. In this page, i will introduce a type of DAC technique, whose name is Delta modulation, that is used in real life. | ||
| + | |||
• Delta modulation | • Delta modulation | ||
| − | + | A practical analog-to-digital conversion technique is delta modulation, whose output is a binary bit sequence, each consisting of either 0 or 1. | |
[[File:LOl12341.png]] | [[File:LOl12341.png]] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 30: | ||
between minimizing slope-overload distortion and granular noise | between minimizing slope-overload distortion and granular noise | ||
| − | • One solution is to reduce | + | • One solution is to reduce 𝑇𝑠, but this increases transmission rate |
Latest revision as of 22:51, 2 December 2017
Data Modulation
In real life, speakers cannot play signals that are in the digital form. In order to play a sound, a physical voltage must be sent to the speakers. However, most soundtracks are now save in digital form in industry, a DAC, digital-to-analog converter, is needed in virtually every device that can produce a sound. In this page, i will introduce a type of DAC technique, whose name is Delta modulation, that is used in real life.
• Delta modulation
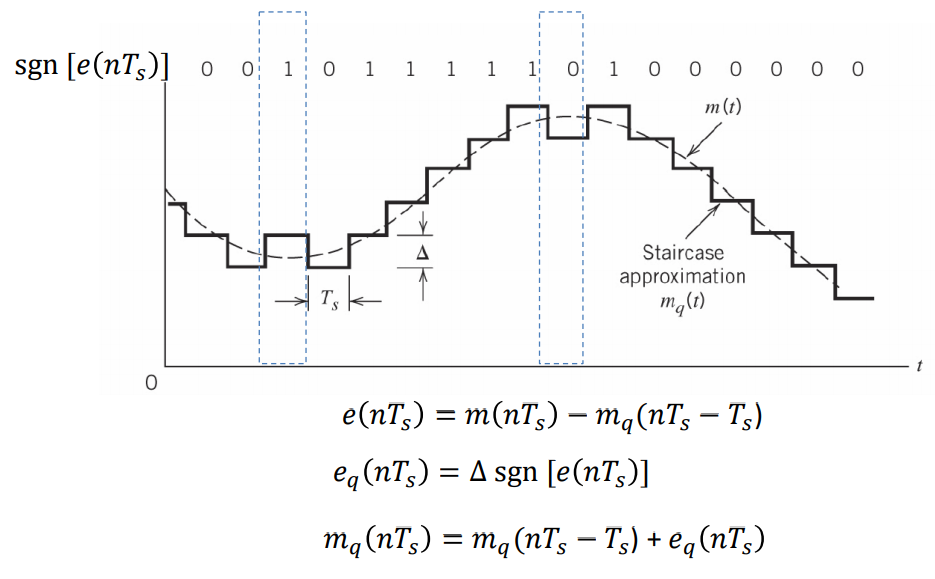
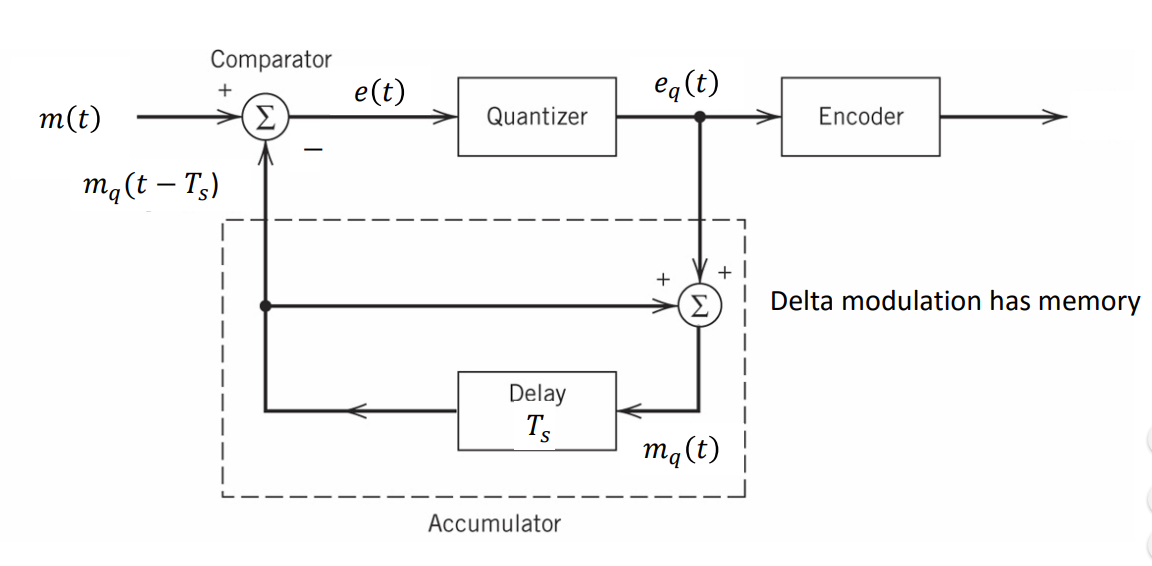
A practical analog-to-digital conversion technique is delta modulation, whose output is a binary bit sequence, each consisting of either 0 or 1.
• Delta modulator at transmitter
• At receiver, the signal can be approximately reconstructed as
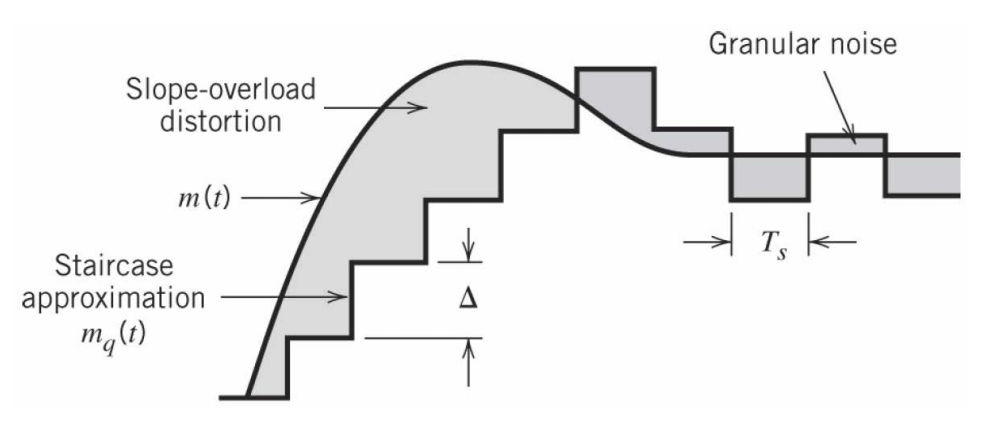
• Two types of distortions: slope-overload distortion and granular noise
• To avoid slope-overload distortion, we need to have
• On the other hand, to reduce granular noise, it is desirable to have smaller ∆
• Thus, there is a trade-off in selecting large or small step size ∆ to balance between minimizing slope-overload distortion and granular noise
• One solution is to reduce 𝑇𝑠, but this increases transmission rate