| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | ==Question== | + | ==Question 1== |
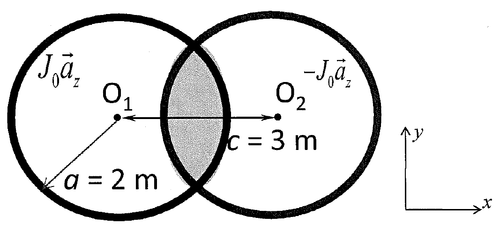
[[Image:Q1FO12013.png|Alt text|500x500px]] | [[Image:Q1FO12013.png|Alt text|500x500px]] | ||
| − | [[Image:Q1FO12013D.png|Alt text| | + | [[Image:Q1FO12013D.png|Alt text|200x200px]] |
=Solution= | =Solution= | ||
| − | + | :'''Click [[ECE_PhD_QE_FO_2013_Problem1.1|here]] to view student [[ECE_PhD_QE_FO_2013_Problem1.1|answers and discussions]]''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Question 2== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | ==Question== | + | |
[[Image:Q2FO12013.png|Alt text|500x500px]] | [[Image:Q2FO12013.png|Alt text|500x500px]] | ||
=Solution= | =Solution= | ||
| − | [[ | + | :'''Click [[ECE_PhD_QE_FO_2013_Problem2.1|here]] to view student [[ECE_PhD_QE_FO_2013_Problem2.1|answers and discussions]]''' |
| − | + | ==Question 3== | |
| − | + | [[Image:Q3FO12013.png|Alt text|500x500px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Q3FO12013D.png|Alt text|500x500px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | =Solution= | ||
| + | :'''Click [[ECE_PhD_QE_FO_2013_Problem3.1|here]] to view student [[ECE_PhD_QE_FO_2013_Problem3.1|answers and discussions]]''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
[[ECE_PhD_Qualifying_Exams|Back to ECE Qualifying Exams (QE) page]] | [[ECE_PhD_Qualifying_Exams|Back to ECE Qualifying Exams (QE) page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:52, 24 April 2017
Fields and Optics (FO)
Question 1: Statics 1
August 2013
Question 1
Solution
- Click here to view student answers and discussions
Question 2
Solution
- Click here to view student answers and discussions
Question 3
Solution
- Click here to view student answers and discussions