| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
===Answer === | ===Answer === | ||
| − | First we know that | + | First we know that <math>V_-</math> = <math>V_+</math><br /> |
| − | + | <math>V_-</math> = 20V = <math>V_+</math> | |
The next step would be to do nodal analysis at the node where the two resistor wires intersect.<br /> | The next step would be to do nodal analysis at the node where the two resistor wires intersect.<br /> | ||
Let's call that node V+:<br /> | Let's call that node V+:<br /> | ||
| − | + | <math>\begin{align} | |
| − | + | \frac{V_+ - 0}{11} + \frac{V_+ - Vout}{44} = & 0\\ | |
| + | \frac{20}{11} + \frac{20 - Vout}{44} = & 0\\ | ||
| + | 80 + 20 - Vout = &0\\ | ||
| + | Vout = 100V | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 26 April 2015
Op Amp Practice
Practice question for ECE201: "Linear circuit analysis I"
By: Chinar Dhamija
Topic: Op Amp
Question
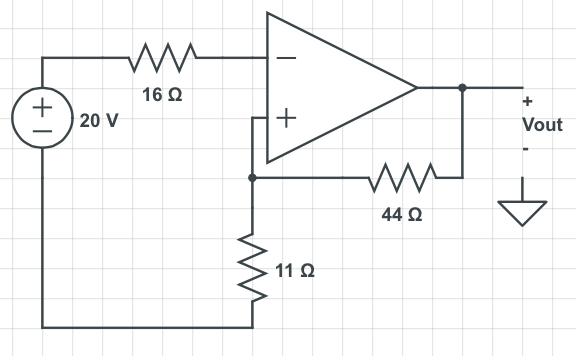
Find the output voltage, Vout.
Answer
First we know that $ V_- $ = $ V_+ $
$ V_- $ = 20V = $ V_+ $
The next step would be to do nodal analysis at the node where the two resistor wires intersect.
Let's call that node V+:
$ \begin{align} \frac{V_+ - 0}{11} + \frac{V_+ - Vout}{44} = & 0\\ \frac{20}{11} + \frac{20 - Vout}{44} = & 0\\ 80 + 20 - Vout = &0\\ Vout = 100V \end{align} $
Questions and comments
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them below
- Comment 1
- Answer to Comment 1
- Comment 2
- Answer to Comment 2