| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
1. Introduction | 1. Introduction | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Sampling is essential to convert analog signal to digital signal. In this page, I would specifically explain about | + | Sampling is essential to convert analog signal to digital signal. In this page, I would specifically explain about downsampling. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | In digital signal processing, the decimator performs decimation, which is | + | In digital signal processing, the decimator performs decimation, which is downsampling a signal. In other words, when a digital |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | signal is | + | signal is downsampled, the signal's sampling rate would be reduced. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:derivation2.jpg]] | [[Image:derivation2.jpg]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | - Frequency domain view of downsampling- | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <math>X2(w) = F(x2[n]) = F(x1[Dn])</math> | ||
3. Example | 3. Example | ||
Revision as of 20:58, 9 October 2014
1. Introduction
Sampling is essential to convert analog signal to digital signal. In this page, I would specifically explain about downsampling.
In digital signal processing, the decimator performs decimation, which is downsampling a signal. In other words, when a digital
signal is downsampled, the signal's sampling rate would be reduced.
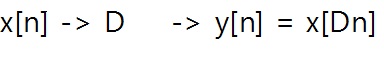
2. Derivation
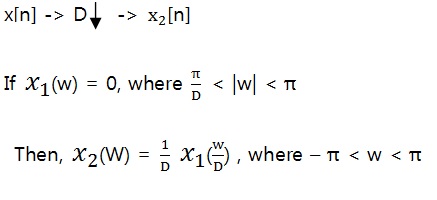
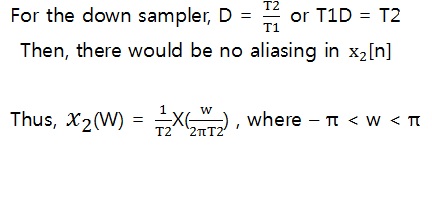
- Frequency domain view of downsampling-
$ X2(w) = F(x2[n]) = F(x1[Dn]) $
3. Example
4. Conclusion

