| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | In this FFT algorithm, the computing of DFT is divided into two levels. First, we compute two 3 | + | In this FFT algorithm, the computing of DFT is divided into two levels. First, we compute two 3-point DFT, which are DFT of even and odd points. |
| − | + | In this step we need 4 times of complex multiplications and 6 times of complex additions for each 3-point DFT. Since we have to do this twice, we need 4*2=8 times of complex multiplications and 6*2=12 times of complex additions. | |
Second, we compute the final DFT by combing the first level result. According to the analysis of Q2, we need N/2=3 times of complex multiplications and N=6 times of complex additions. | Second, we compute the final DFT by combing the first level result. According to the analysis of Q2, we need N/2=3 times of complex multiplications and N=6 times of complex additions. | ||
| − | In total, we need | + | In total, we need 8+3=11 times of complex multiplications and 12+6=18 times of complex additions. |
2) | 2) | ||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
[[Image:diagramFFT2.jpg]] | [[Image:diagramFFT2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Analytical Expressions: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \begin{align} | ||
| + | X_N(k)&=\sum_{n=0}^{5} x(n)e^{-\frac{j2\pi kn}{6}} \\ | ||
| + | &\text{Change variable n=3m+l, m=0,1; l=0,1,2 } \\ | ||
| + | X_N(k)&=\sum_{l=0}^{2}\sum_{m=0}^{1}x(3m+l)e^{-\frac{j2\pi k(3m+l)}{6}} \\ | ||
| + | &=\sum_{l=0}^{2}e^{-\frac{j2\pi kl}{6}}\sum_{m=0}^{1}x(3m+l)e^{-\frac{j2\pi km)}{2}} \\ | ||
| + | &=\sum_{l=0}^{2}W_N^{kl}X_l(k) \text{k=0,1,...,5 } | ||
| + | \end{align} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
In this FFT algorithm, the computing of DFT is still divided into two levels. However, we will first compute three 2 points DFT, which are DFT of the first half points and the second half points. According to analysis of Q2, we need N/2=3 times of complex | In this FFT algorithm, the computing of DFT is still divided into two levels. However, we will first compute three 2 points DFT, which are DFT of the first half points and the second half points. According to analysis of Q2, we need N/2=3 times of complex | ||
multiplications and N=6 times of complex additions. | multiplications and N=6 times of complex additions. | ||
| − | Second, we compute the two 3 points DFT using first level result. | + | Second, we compute the two 3 points DFT using first level result. we need 4 times of complex multiplications and 6 times of complex additions for each 3-point DFT. Since we have to do this twice, we need 4*2=8 times of complex multiplications and 6*2=12 times of complex additions. |
| − | In total, we need 3+ | + | In total, we need 3+8=11 times of complex multiplications and 6+12=18 times of complex additions. |
Notice that the output sequences of DFT of 2) is different from 1). | Notice that the output sequences of DFT of 2) is different from 1). | ||
Revision as of 17:33, 19 October 2010
Homework 6 Solution
Q1.
Matlab code:
Assign the value of parameters and then call the function signalDFT
For example, in case 6 type following command in the command window of Matlab:
N=20;
w1=0.62831853;
k=0.2;
w2=0.79168135;
[x,X]=signal(w1,w2,k,N);
Plot result:
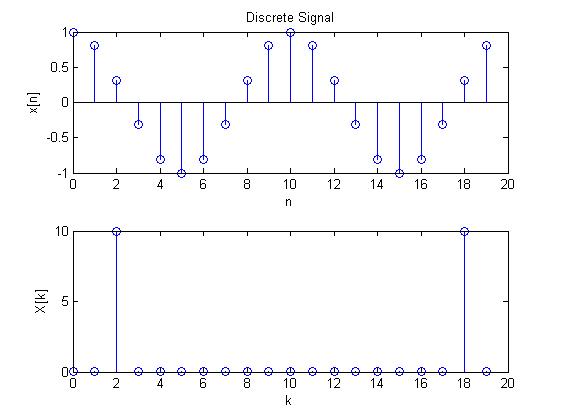
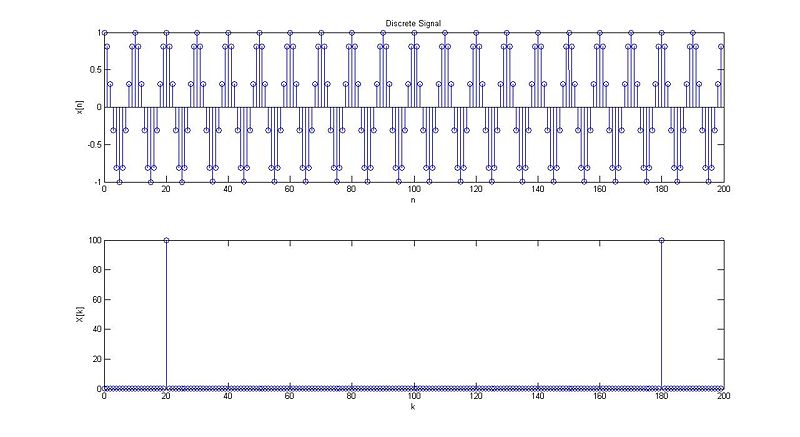
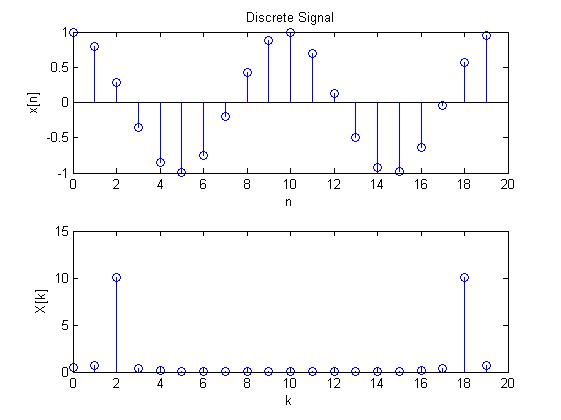
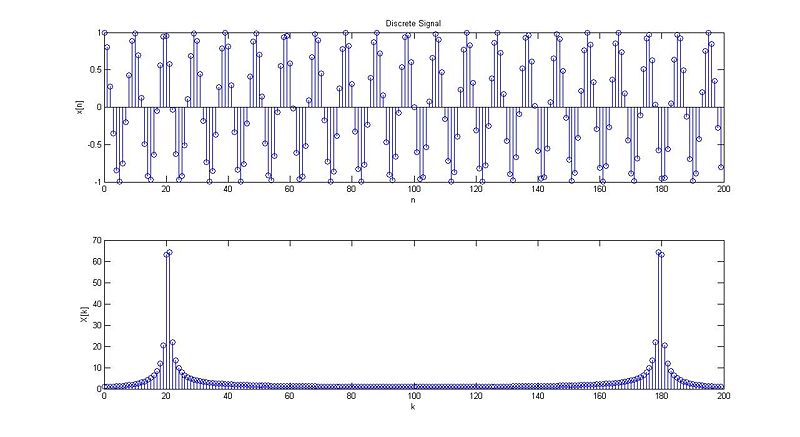
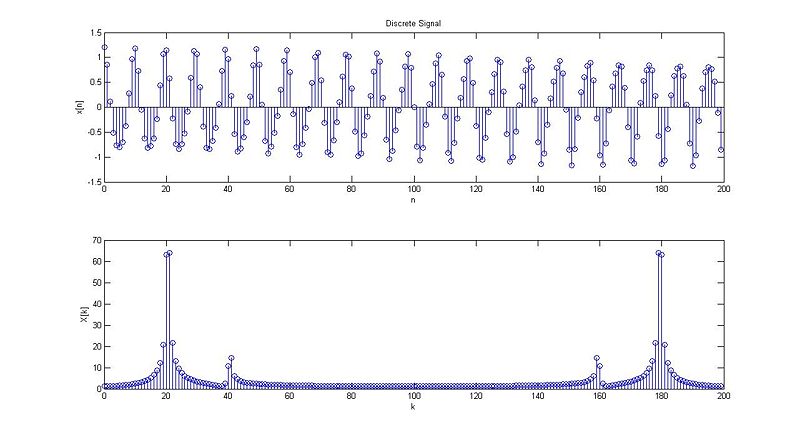
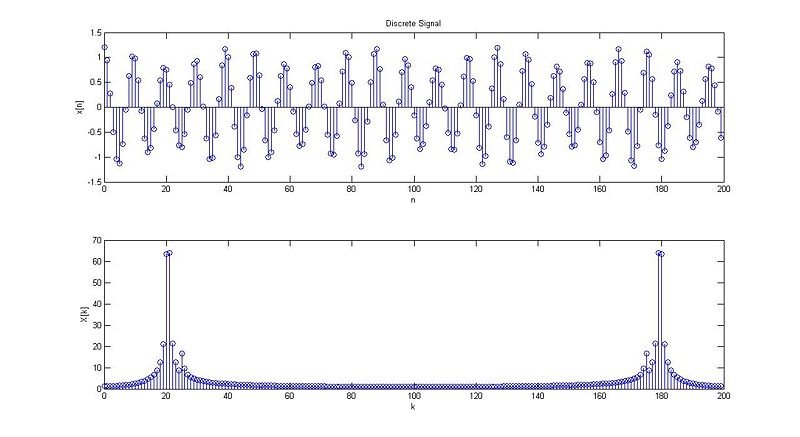
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
case 6:
Q2.
Recall the definition of DFT: $ X[k]=\sum_{n=0}^{N-1} x[n]e^{-j2\pi k/N} $
In this question N=8
If we use summation formula to compute DFT, for each k, we need N times complex multiplications and N times complex additions.
In total, we need N*N=64 times of complex multiplications and N*(N-1)=56 times of complex additions.
In decimation-in-time FFT algorithm, we keep on decimating the number of points by 2 until we get 2 points DFT. At most, we can decimate $ v=log_2 N $ times. As a result, we get v levels of DFT. For each level, we need N/2 times of complex multiplications and N times of complex additions.
In total, we need $ \frac{N}{2}log_2 N=12 $N times of complex multiplications and $ Nlog_2 N=24 $ times of complex additions.
Q3.
Denote N is the points number of the input signal's DFT. Then N=6.
1) The normal DFT algorithm: If we use summation formula to compute DFT, according to the analysis of Q2. We need N*N=36 times of complex multiplications and N*(N-1)=30 times of complex additions.
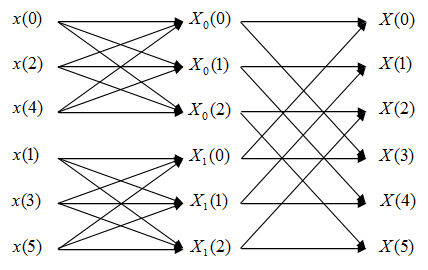
Flow diagram of FFT:
Analytical Expressions:
$ \begin{align} X_N(k)&=\sum_{n=0}^{5} x(n)e^{-\frac{j2\pi kn}{6}} \\ &\text{Change variable n=2m+l, m=0,1,2; l=0,1 } \\ X_N(k)&=\sum_{l=0}^{1}\sum_{m=0}^{2}x(2m+l)e^{-\frac{j2\pi k(2m+l)}{6}} \\ &=\sum_{l=0}^{1}e^{-\frac{j2\pi kl}{6}}\sum_{m=0}^{2}x(2m+l)e^{-\frac{j2\pi km)}{3}} \\ &=\sum_{l=0}^{1}W_N^{kl}X_l(k) \text{k=0,1,...,5 } \end{align} $
In this FFT algorithm, the computing of DFT is divided into two levels. First, we compute two 3-point DFT, which are DFT of even and odd points.
In this step we need 4 times of complex multiplications and 6 times of complex additions for each 3-point DFT. Since we have to do this twice, we need 4*2=8 times of complex multiplications and 6*2=12 times of complex additions.
Second, we compute the final DFT by combing the first level result. According to the analysis of Q2, we need N/2=3 times of complex multiplications and N=6 times of complex additions.
In total, we need 8+3=11 times of complex multiplications and 12+6=18 times of complex additions.
2)
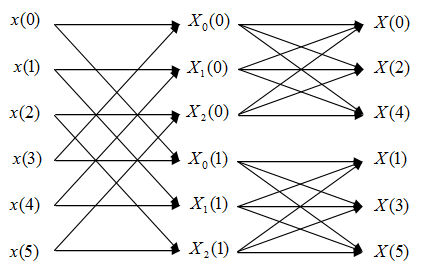
Flow diagram of FFT:
Analytical Expressions:
$ \begin{align} X_N(k)&=\sum_{n=0}^{5} x(n)e^{-\frac{j2\pi kn}{6}} \\ &\text{Change variable n=3m+l, m=0,1; l=0,1,2 } \\ X_N(k)&=\sum_{l=0}^{2}\sum_{m=0}^{1}x(3m+l)e^{-\frac{j2\pi k(3m+l)}{6}} \\ &=\sum_{l=0}^{2}e^{-\frac{j2\pi kl}{6}}\sum_{m=0}^{1}x(3m+l)e^{-\frac{j2\pi km)}{2}} \\ &=\sum_{l=0}^{2}W_N^{kl}X_l(k) \text{k=0,1,...,5 } \end{align} $
In this FFT algorithm, the computing of DFT is still divided into two levels. However, we will first compute three 2 points DFT, which are DFT of the first half points and the second half points. According to analysis of Q2, we need N/2=3 times of complex multiplications and N=6 times of complex additions.
Second, we compute the two 3 points DFT using first level result. we need 4 times of complex multiplications and 6 times of complex additions for each 3-point DFT. Since we have to do this twice, we need 4*2=8 times of complex multiplications and 6*2=12 times of complex additions.
In total, we need 3+8=11 times of complex multiplications and 6+12=18 times of complex additions.
Notice that the output sequences of DFT of 2) is different from 1).
Compare 1) and 2), both methods have the same amount of complex operations.
Q4.
Q5.
Q6.
Q7.