| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A periodic function is a function that repeats its values after some definite period has been added to its independent variable. This property is called periodicity. | + | =Periodic versus non-periodic functions ([[Homework_1_ECE301Fall2008mboutin|hw1]], [[ECE301]])= |
| + | <span style="color:green"> Read the instructor's comments [[hw1periodicECE301f08profcomments|here]]. </span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''A periodic function''' is a function that repeats its values after some definite period has been added to its independent variable. This property is called periodicity. | ||
For a function on the real numbers or on the integers, that means that the entire graph can be formed from copies of one particular portion, repeated at regular intervals. More explicitly, a function f is periodic with period P greater than zero if | For a function on the real numbers or on the integers, that means that the entire graph can be formed from copies of one particular portion, repeated at regular intervals. More explicitly, a function f is periodic with period P greater than zero if | ||
| Line 11: | Line 14: | ||
A plot of f(x) = sin(x) and g(x) = cos(x); both functions are periodic with period 2π.A simple example of a periodic function is the function f that gives the "fractional part" of its argument. Its period is 1. In particular, | A plot of f(x) = sin(x) and g(x) = cos(x); both functions are periodic with period 2π.A simple example of a periodic function is the function f that gives the "fractional part" of its argument. Its period is 1. In particular, | ||
| − | f( 0.5 ) = f( 1.5 ) = f( 2.5 ) = ... = 0.5. [[Image:Example_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | + | f( 0.5 ) = f( 1.5 ) = f( 2.5 ) = ... = 0.5. [[Image:Example_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] |
| + | |||
| + | '''Non periodic signal''' is a signal that doesnt repeat its values after some definite period has been added to its independent variable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example of a non periodic signal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | q) Is cos(n) a periodic signal ? | ||
| + | |||
| + | we want a integer N such that | ||
| + | cos (n+N) = cos (n) for all n | ||
| + | |||
| + | N is a multiple of 2*pi but since no integer multiple of 2*pi is an integer Therefore cos (n) is not periodic | ||
Latest revision as of 06:03, 14 April 2010
Periodic versus non-periodic functions (hw1, ECE301)
Read the instructor's comments here.
A periodic function is a function that repeats its values after some definite period has been added to its independent variable. This property is called periodicity.
For a function on the real numbers or on the integers, that means that the entire graph can be formed from copies of one particular portion, repeated at regular intervals. More explicitly, a function f is periodic with period P greater than zero if
f(x + P) = f(x) for all values of x in the domain of f. An aperiodic function (non-periodic function) is one that has no such period P (not to be confused with an antiperiodic function (below) for which f(x + P) = −f(x) for some P).
If a function f is periodic with period P, then for all x in the domain of f and all integers n,
f(x + nP) = f(x).
A plot of f(x) = sin(x) and g(x) = cos(x); both functions are periodic with period 2π.A simple example of a periodic function is the function f that gives the "fractional part" of its argument. Its period is 1. In particular,
f( 0.5 ) = f( 1.5 ) = f( 2.5 ) = ... = 0.5. 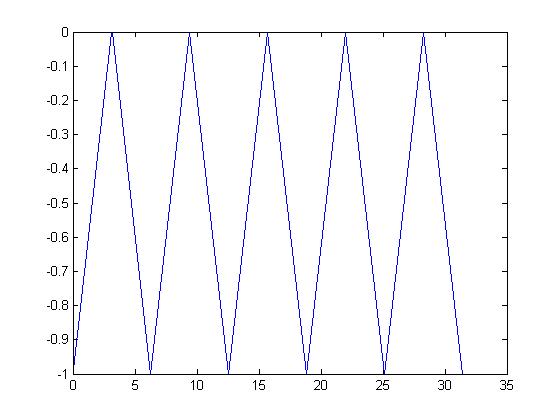
Non periodic signal is a signal that doesnt repeat its values after some definite period has been added to its independent variable.
Example of a non periodic signal.
q) Is cos(n) a periodic signal ?
we want a integer N such that cos (n+N) = cos (n) for all n
N is a multiple of 2*pi but since no integer multiple of 2*pi is an integer Therefore cos (n) is not periodic

