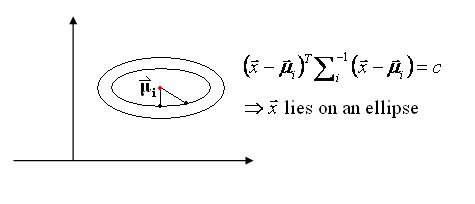| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
[[Image: Lc5_ellipse_OldKiwi.jpg]] | [[Image: Lc5_ellipse_OldKiwi.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Lectures == | ||
| + | [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_1_-_Introduction 1] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_2_-_Decision_Hypersurfaces 2] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_3_-_Bayes_classification 3] | ||
| + | [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_4_-_Bayes_Classification 4] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_5_-_Discriminant_Functions 5] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_6_-_Discriminant_Functions 6] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_7_-_MLE_and_BPE 7] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_8_-_MLE%2C_BPE_and_Linear_Discriminant_Functions 8] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_9_-_Linear_Discriminant_Functions 9] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_10_-_Batch_Perceptron_and_Fisher_Linear_Discriminant 10] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_11_-_Fischer%27s_Linear_Discriminant_again 11] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_12_-_Support_Vector_Machine_and_Quadratic_Optimization_Problem 12] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_13_-_Kernel_function_for_SVMs_and_ANNs_introduction 13] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_14_-_ANNs%2C_Non-parametric_Density_Estimation_%28Parzen_Window%29 14] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_15_-_Parzen_Window_Method 15] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_16_-_Parzen_Window_Method_and_K-nearest_Neighbor_Density_Estimate 16] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_17_-_Nearest_Neighbors_Clarification_Rule_and_Metrics 17] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_18_-_Nearest_Neighbors_Clarification_Rule_and_Metrics%28Continued%29 18] | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 20 March 2008
LECTURE THEME : - Discriminant Functions
Discriminant Functions: one way of representing classifiers
Given the classes $ \omega_1, \cdots, \omega_k $
The discriminant functions $ g_1(x),\ldots, g_K(x) $ such that $ g_i(x) $ n-dim S space $ \rightarrow \Re $
which are used to make decisions as follows:
decide $ \omega_i $ if $ g_i(x) \ge g_j(x), \forall j $
Note that many different choices of $ g_i(x) $ will yield the same decision rule, because we are interested in the order of values of $ g_i(x) $ for each x, and not their exact values.
For example: $ g_i(x) \rightarrow 2(g_i(x)) $ or $ g_i(x) \rightarrow ln(g_i(x)) $
In other words, we can take $ g_i(x) \rightarrow f(g_i(x)) $ for any monotonically increasing function f.
Relation to Bayes Rule
e.g. We can take $ g_i(\mathbf(x)) = P(\omega_i|\mathbf(x)) $
then $ g_i(\mathbf(x)) > g_j(\mathbf(x)), \forall j \neq i $
$ \Longleftrightarrow P(w_i|\mathbf(X)) > P(w_j|\mathbf(X)), \forall j \neq i $
OR we can take
$ g_i(\mathbf(x)) = p(\mathbf(x)|\omega_i)P(\omega_i) $
then $ g_i(\mathbf(x)) > g_j(\mathbf(x)), \forall j \neq i $
$ \Longleftrightarrow g_i(\mathbf(x)) = ln(p(\mathbf(x)|\omega_i)P(\omega_i)) = ln(p(\mathbf(x)|\omega_i))+ln(P(\omega_i) $
OR we can take
$ g_i(\mathbf(x)) = ln(p(\mathbf(x)|\omega_i)P(\omega_i)) = ln(p(\mathbf(x)|\omega_i))+ln(P(\omega_i) $
We can take any $ g_i $ as long as they have the same ordering in value as specified by Bayes rule.
Some useful links:
- Bayes Rule in notes: https://engineering.purdue.edu/people/mireille.boutin.1/ECE301kiwi/Lecture4
- Bayesian Inference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayesian_inference
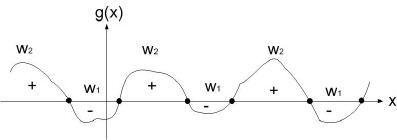
Relational Decision Boundary
Ex : take two classes $ \omega_1 $ and $ \omega_2 $
$ g(\vec x)=g_1(\vec x)-g_2(\vec x) $
decide $ \omega_1 $ when $ g(\vec x)>0 $
and $ \omega_2 $ when $ g(\vec x)<0 $
when $ g(\vec x) = 0 $, you are at the decision boundary ( = hyperplane)
$ \lbrace \vec x | \vec x \;\;s.t \;\;g(\vec x)=0\rbrace $ is a hypersurface in your feature space i.e a structure of co-dimension one less dimension than space in which $ \vec x $ lies
Discriminant function for the Normal Density
Suppose we assume that the distribution of the feature vectors is such that the density function p(X|w) is normal for all i.
Eg: Length of hair among men is a normal random variable. Same for hairlength in women. Now we have: