(→Problem 7) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[Category: ECE]] | |
| + | [[Category: ECE 301]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Summer]] | ||
| + | [[Category: 2008]] | ||
| + | [[Category: asan]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Exams]] | ||
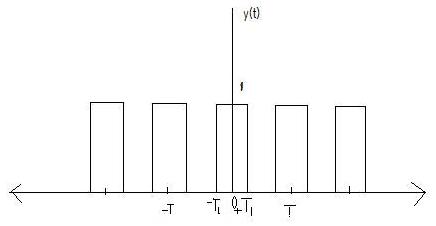
Determine the Fourier Series co-efficient for the following continuous time periodic signals.Show the details of your calculations and simplify your answers. | Determine the Fourier Series co-efficient for the following continuous time periodic signals.Show the details of your calculations and simplify your answers. | ||
| − | [[Image:ECE301Summer2008_San_Exam1_P7_Fig1.jpg]] | + | [[Image:ECE301Summer2008_San_Exam1_P7_Fig1-2.jpg]] |
<math>a_{k} = 1/T \int_{T} x(t) e^{-jkw_{o}t} dt</math> | <math>a_{k} = 1/T \int_{T} x(t) e^{-jkw_{o}t} dt</math> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 33: | ||
<math>= \frac{2T_{1}}{T}</math> | <math>= \frac{2T_{1}}{T}</math> | ||
| − | [[Problem 7 Part b]] | + | [[Problem 7 Part b_(ECE301Summer2008asan)|Problem 7 Part b]] |
Latest revision as of 10:05, 21 November 2008
Determine the Fourier Series co-efficient for the following continuous time periodic signals.Show the details of your calculations and simplify your answers.
$ a_{k} = 1/T \int_{T} x(t) e^{-jkw_{o}t} dt $
$ = 1/T \int_{-T_{1}} ^ {T_{1}} 1*e^{-jk2\frac{\pi}{T} t} dt $ (x(t)=1) $ = 1/T \int_{-T_{1}} ^ {T_{1}} e^{-jk2\frac{\pi}{T} t} dt $
$ = 1/T [\frac{e^{-jk2\frac{\pi}{T} t}}{-jk2\frac{\pi}{T}}]_{-T_{1}} ^ {T_{1}} $
$ = \frac{-1}{jk2\pi} (e^{-jk2\frac{\pi}{T} T_{1}} - e^{jk2\frac{\pi}{T} T_{1}}) $
$ = \frac{1}{k\pi} (Sin(\frac{2k\pi}{T} T_{1}) $
Now For K = 0 Condition
$ a_{k} = 1/T \int_{T} x(t) e^{-jkw_{o}t} dt $
PUT THE VALUE K=0 IN ABOVE EQUATION
$ = 1/T \int_{-T_{1}} ^ {T_{1}} 1 dt $ $ = \frac{T_{1} + T_{1}}{T} $
$ = \frac{2T_{1}}{T} $