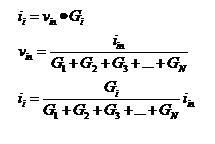ECE 201 Topic List
Concepts:
1. Current in terms of charge (q):
i(t) = ∆q/∆t = dq/dt (also found in ECE 311)
2. Ohm’s Law:
V = I*R (also found in ALL ECE COURSES)
3. Work :– difference in energy = W1 – W2 (also fond in ECE 311)
Voltage = energy divided by charge (W1-W2)/Q
Q = I*t
P = V*I
4. Kirchoff’s Current Law :– at any node in an electrical circuit, the sum of currents flowing into the node is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of the node. (also found in ECE 202, ECE 255)
(Kirchoff’s Circuit Laws. (n.d.) In Wikipedia. Retrieved March 23, 2010 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kirchhoff%27s_circuit_laws)
5. Kirchoff’s Voltage Law: – the sum of the voltages in any closed loop is equivalent to the sum of potential drops in that loop
[Kirchoff’s Circuit Laws. (n.d.) In Wikipedia. Retrieved March 23, 2010 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kirchhoff%27s_circuit_laws]
6. Voltage Division (also found in ECE 202, ECE 255, ECE 382, ECE 402)
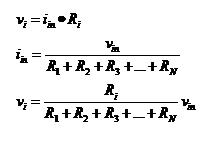
(Qi, Minghao (2007, Fall) ECE 201 Notes Retrieved March 18,2010 from http://cobweb.ecn.purdue.edu/~ece201/handouts/Lecture_notes_Qi/Index.html)
7. Equivalent Parallel Resistance (also found in ECE 202, ECE 255, ECE 382, ECE 402)
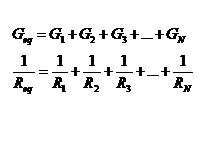
(Qi, Minghao (2007, Fall) ECE 201 Notes Retrieved March 18,2010 from http://cobweb.ecn.purdue.edu/~ece201/handouts/Lecture_notes_Qi/Index.html)
9. Nodal Analysis :- a method of determining the voltage between nodes in an electrical circuit in terms of the branch current
(Nodal Analysis. (n.d.) In Wikipedia. Retrieved March 23, 2010 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nodal_analysis)
10. Mesh Analysis :- a method to determine the voltage and currents at various parts of a circuit
11. Superposition theorem:- the response in any branch of a linear circuit having more than one independent source is equivalent to the algebraic sum of the responses caused by each independent source acting alone.
(Superposition Theorem. (n.d.) In Wikipedia. Retrieved March 23, 2010 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superposition_theorem)
12. Source transformations :- a technique in which independent current sources can be transformed into independent voltage sources (and vice versa)
13. Thevenin’s Theorem:- states any combination of resistors, voltage and current sources can be modeled by a single voltage source and resistor in series
14. Norton’s Theorem:- states any combination of resistors, voltage and current sources can be modeled by a single current source connected in parallel with a resistor