Communication Networks Signal and Image processing (CS)
Problem 1,2
Solution 1:
a)
$ {{P}_{0}}({{e}^{j\omega }})=\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{{{p}_{0}}(n){{e}^{-jn\omega }}}=\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{\left( \sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)} \right){{e}^{-jn\omega }}}=\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)}{{e}^{-j(m0+n\omega )}}=X({{e}^{j0}},{{e}^{j\omega }})} $
b)
$ {{P}_{1}}({{e}^{j\omega }})=\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{{{p}_{1}}(m){{e}^{-jm\omega }}}=\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{\left( \sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)} \right){{e}^{-jm\omega }}}=\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)}{{e}^{-j(m\omega +n0)}}=X({{e}^{j\omega }},{{e}^{j0}})} $
c)
$ \sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{{{p}_{0}}(n)}=\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{\left( \sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)} \right)}=\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)}{{e}^{-j(m0+n0)}}=X({{e}^{j0}},{{e}^{j0}})} $
d)
No, they don’t. From part (a) and (b), we know that $ {{P}_{0}}({{e}^{jw}}) $ and $ {{P}_{1}}({{e}^{jw}}) $ represent the horizontal and vertical axes of the 2D DSFT $ X({{e}^{j\mu }},{{e}^{j\upsilon }}) $, which is not enough for reconstruction of x(m, n).
For example, $ {{x}_{1}}(m,n)=\left( \begin{matrix} 1 & 3 \\ 2 & 4 \\ \end{matrix} \right),_{{}}^{{}} and\ {{x}_{2}}(m,n)=\left( \begin{matrix} 0 & 4 \\ 3 & 3 \\ \end{matrix} \right) $ have the same $ {{p}_{0}}(n)=\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & 7 \\ \end{matrix} \right]\ and\ {{p}_{1}}(m)=\left[ \begin{matrix} 4 \\ 6 \\ \end{matrix} \right] $. So, x(m,n) can’t be reconstructed from $ {{p}_{0}}(n)\ and\ {{p}_{1}}(m) $.
Solution 2:
a)
$ {{P}_{0}}({{e}^{j\omega }})=\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)} {{e}^{-jn\omega }}}=X({{e}^{j0}},{{e}^{j\omega }}) $
The answer is correct, but multiple steps are skipped in this solution, which are necessary for clarity. (See Solution 1)
b)
$ {{P}_{1}}({{e}^{j\omega }})=\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)}{{e}^{-jm\omega }}}=X({{e}^{j\omega }},{{e}^{j0}}) $
The answer is correct, but multiple steps are skipped in this solution, which are necessary for clarity. (See Solution 1)
c)
$ \sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{{{p}_{0}}(n)}=\sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)}=X({{e}^{j0}},{{e}^{j0}})} $
The answer is correct, but multiple steps are skipped in this solution, which are necessary for clarity. (See Solution 1)
d)
They do not; $ {{p}_{0}}(n)\ and\ {{p}_{1}}(m) $ are projections at two angles, and do not contain enough information to reconstruct x(m,n).
$ \begin{align} & X({{e}^{j\mu }},{{e}^{j\upsilon }})=\sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{\left[ \sum\limits_{n=-\infty }^{\infty }{x(m,n)} \right]}{{e}^{-jm\mu }}{{e}^{-jn\upsilon }} \\ & X({{e}^{j\mu }},{{e}^{j\upsilon }})\ne \sum\limits_{m=-\infty }^{\infty }{{{p}_{1}}(m)}{{e}^{-jm\mu }}{{e}^{-jn\upsilon }}\ne {{P}_{1}}({{e}^{j\mu }}){{e}^{-jn\upsilon }} \\ & \Rightarrow Can't\ do\ it! \end{align} $
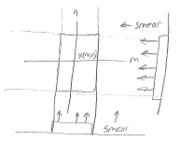
- To form reconstruction, need projections along many angles.
- Could reconstruct a very simple object, like triangle.
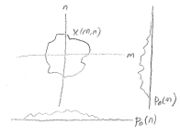
In the first figure, the projection of x(m,n) along the vertical axis is $ {{p}_{1}}(m)\ $, not $ \ {{p}_{0}}(m) $.
In the second line of equations, $ = $ must be used instead of $ \ne $.
Also, the question asks for a counter example if the answer is no!
Related Problem
Consider the 2D discrete space signal x(m,n) with the DSFT of X(ejμ,ejν) given by
$ X(e^{j\mu},e^{j\nu}) = \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} x(m,n)e^{-j(m\mu+n\nu)} $
Then define
$ p_{0}(n) = \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty}x(m,n) $
$ p_{1}(m) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}x(m,n) $
with corresponding DTFT given by
$ P_{0}(e^{j\omega}) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} p_{0}(n)e^{-jn\omega} $
$ P_{1}(e^{j\omega}) = \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} p_{0}(m)e^{-jm\omega} $
a) Derive an expression for P0(ejω) in terms of X(ejμ,wjν).
b) Derive an expression P0(ejω) in terms of X(ejμ,ejν).
c) Find a function x(m,n) that is not zero everywhere such that $ {{p}_{0}}(n)={{p}_{1}}(m)=0 $ for all m and n.
d) Do the function p0(n) and p1(m) together contain sufficient information to uniquely reconstruct the function x(m,n)? Justify your answer.
(Refer to ECE 637 Spring 2015 Exam 1 Problem 2.)