1)
a)
$ \bar{E} = E_0e^{-j\beta z \hat{y}}\\ \bar{H} = \frac{E_0}{n_0}e^{-j\beta z \hat{x}}\hspace{1cm} n_0=\sqrt{\frac{\mu_0}{\epsilon_0}} \\ \bar{H} = E_0 \sqrt{\frac{\epsilon}{\mu}}\cos(6\pi\cdot10^9t-\beta z)(-\hat{x})\\ \begin{vmatrix}\hat{x} & \hat{y} & \hat{z}\\\frac{\partial}{\partial x}&\frac{\partial}{\partial y}&\frac{\partial}{\partial z}\\0&E_y&0\end{vmatrix}\\ $
also: $ \nabla\times\bar{E} = -j\omega\mu_0\bar{H} $
$ \begin{align*} \bar{H} &= \frac{j}{\omega\mu}[\nabla\times\hat{y}E_0e^{-j\beta z}]\\ \bar{H} &= \frac{j}{\omega\mu_0}\bigg[\hat{x}\bigg(-\frac{\partial}{\partial z}E_0e^{-j\beta z}\bigg)\bigg]\\ \bar{H} &= \frac{j}{\omega\mu_0}[\hat{x}(j\beta)E_0e^{-j\beta z}]\\ \bar{H} &= (-\hat{x})\sqrt{\frac{\epsilon}{\mu_0}}E_0e^{-j\beta z}\\ \end{align*} $
b)
$ \beta = \omega\sqrt{\mu_0\epsilon_0} = \frac{\omega}{c} = \frac{6\pi\cdot10^9}{3\cdot10^8} = 2\pi(10)\\ \beta = 20\pi 1/m\\ \beta = \frac{2\pi}{\lambda} \to \lambda = \frac{2\pi}{\beta} = \frac{2\pi}{20\pi} = \frac{1}{10}\\ \lambda = \frac{1}{10}m\\ $
2)
a) $ \nabla\times\bar{E} = -\frac{d\bar{B}}{dt} = \begin{vmatrix}\hat{x} & \hat{y} & \hat{z}\\\frac{\partial}{\partial y}&\frac{\partial}{\partial y}&\frac{\partial}{\partial z}\\0&E_y&0\end{vmatrix} = (-\hat{x})\frac{2E_y}{2z} + \hat{z}\bigg(\frac{2E_y}{2x}\bigg)\\ -\mu_0\frac{d\bar{H}}{dt} = (-\hat{x})[\beta E_0\sin(10\pi x)\sin(\omega t-\beta z)] + (\hat{z})[E_0(10\pi)\cos(10\pi x)\cos(\omega t-\beta z)]\\ \bar{H} = (\hat{x})\bigg[-\frac{\beta E_0}{\mu_0\omega}\sin(10\pi x)\cos(\omega t-\beta z)\bigg] + (\hat{z})\bigg[\frac{E_0(10\pi)}{\omega}\cos(10\pi x)\sin(\omega t-\beta z)\bigg]\\ \bar{H} = (-\hat{x})\bigg[E_0\sqrt{\frac{\epsilon_0}{\mu_0}}\sin(10\pi x)\cos(6\pi\cdot10^9 t-\beta z)\bigg] + (\hat{z})\bigg[E_0\bigg(\frac{5}{3}\cdot10^{-9}\bigg)\cos(10\pi x)\sin(6\pi\cdot10^9 t-\beta z)\bigg]\\ $ $ z- $variation is small for large frequency
--- modulated plane wave
b)
$ \beta = \omega\sqrt{\mu_0\epsilon_0} = \frac{\omega}{c} = 20\pi1/m\\ $
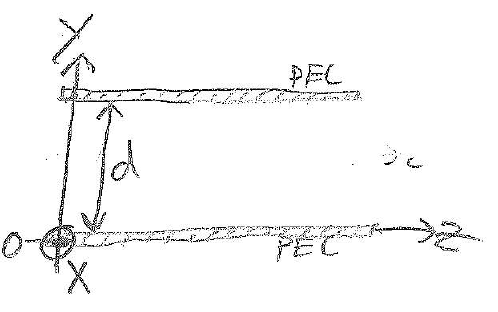
c)d)
\underline{trivial}: d$ \to \infty $ - $ \bar{E} $ must be $ \perp $ to PEC\\ - $ \bar{H} $ must be tangent to PEC\\
\underline{at PEC}: $ \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} E_{1t} = E_{2t} = 0\\ D_{in} = P_s\\ B_{in} =0\\ H_{1t} = J_s \end{array} \right.\\ $
- want TM$ _0 $ = TEM mode of parallel-plate waveguide to propagate - also consider: $ 10\pi x = 2\pi \to d = \frac{1}{5} $ along $ x? \to B_{in} \ne 0 $
3)
$ \int_V \bigg[\underset{a)}{\frac{\partial}{\partial t}\bigg(\frac{\mu\bar{H}\cdot\bar{H}}{2}\bigg)} +\underset{b)}{\frac{\partial}{\partial t}\bigg(\frac{\epsilon\bar{E}\cdot\bar{E}}{2}\bigg)} + \underset{c)}{\bar{E}\cdot\bar{J}\bigg]}dV = -\oint_S\underset{d)}{(\bar{E}\times\bar{H})}\cdot d\bar{s}\\ $
a) rate of increase over time of stored magnetic energy within the volume. Units are: $ \frac{}{} = \big(\frac{\omega}{S} = J\big) = W $
b) rate of increase over time of stored electric energy within the volume. Units are: $ \frac{}{} = \big(\frac{\omega}{S} = J\big) = W $
c) power due to current within volume; usually due to conduction current ($ \bar{J} = \sigma \bar{E} $) constituting ohmic loss. Can also have convection current ($ \bar{J} = P_v\bar{u} $ where $ \bar{u} $ is velocity). Units are $ (W) $
d) total power flowing \underline{into} a closed surface $ S $ with volume $ V $. By conservation of energy, this must equal the terms on the right. Units are $ W $
4) $ \omega^2\mu\epsilon = \bigg(\frac{m\pi}{a}\bigg)^2 + \bigg(\frac{n\pi}{b}\bigg)^2 + \bigg(\frac{p\pi}{d}\bigg)^2 \hspace{1cm}\nabla\times\bar{E} = -j\omega\mu\bar{H}\to\lambda \\ f = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{\mu_0\epsilon_0}}\sqrt{ \bigg(\frac{m}{a}\bigg)^2 + \bigg(\frac{n}{b}\bigg)^2 + \bigg(\frac{p}{d}\bigg)^2 }\\ \lambda = \frac{c}{f} = \frac{2}{\sqrt{\big(\frac{m}{a}\big)^2 + \big(\frac{n}{b}\big)^2 + \big(\frac{p}{d}\big)^2}}\\ \lambda = \frac{2}{\sqrt{\big(\frac{1}{a}\big)^2 + \big(\frac{p}{d}\big)^2}}\\ $